GPU対応PyTorch 2.3のセットアップと性能確認(Windows 上)
【概要】
Windows環境でのPyTorch 2.3のインストール手順と動作確認方法を詳細に説明している.主な内容としては,Build Tools for Visual Studio 2022,NVIDIAドライバ,NVIDIA CUDAツールキット,NVIDIA cuDNNの事前インストール,PyTorch公式ページ https://pytorch.org/ からのインストールコマンド取得,コマンドプロンプトでの実行である.また,インストール後の動作確認として,GPUとCPUの性能比較を行う行列積計算プログラムの実行方法が示されている.さらに,画像分類タスクのためのImageNetで学習済みのConvNeXtBaseモデルを用いたリアルタイム画像分類プログラムの実装例も提供されている.各ステップでは,具体的なコマンドラインの操作を示している.
【目次】
【サイト内の関連ページ】
【付記】 本ページのプログラムはAIのアシストを受けて作成しています
前準備
Python 3.12 のインストール
インストール済みの場合は実行不要。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要である。
REM Python をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements
REM Python のパス設定
set "PYTHON_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312"
set "PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312\Scripts"
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_PATH%" /M >nul
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" /M >nul【関連する外部ページ】
Python の公式ページ: https://www.python.org/
AI エディタ Windsurf のインストール
Pythonプログラムの編集・実行には、AI エディタの利用を推奨する。ここでは,Windsurfのインストールを説明する。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行して、Windsurfをシステム全体にインストールする。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
winget install --scope machine --id Codeium.Windsurf -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements【関連する外部ページ】
Windsurf の公式ページ: https://windsurf.com/
Visual Studio 2022 Build Toolsとランタイムのインストール
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要である。
REM Visual Studio 2022 Build Toolsとランタイムのインストール
winget install --scope machine --wait --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements Microsoft.VisualStudio.2022.BuildTools Microsoft.VCRedist.2015+.x64
REM インストーラーとインストールパスの設定
set VS_INSTALLER="C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\Installer\vs_installer.exe"
set VS_PATH="C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\BuildTools"
REM C++開発ワークロードのインストール(次のコマンドは全体で1行である)
%VS_INSTALLER% modify --installPath %VS_PATH% --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Workload.VCTools --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Tools.x86.x64 --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.Windows11SDK.22621 --includeRecommended --quiet --norestart
NVIDIA ドライバのインストール(Windows 上)
NVIDIA ドライバ
NVIDIA ドライバは,NVIDIA製GPUを動作させるための重要なソフトウェアである.このドライバをインストールすることにより,GPUの性能を引き出すことができ,グラフィックス関連のアプリ,AI関連のアプリの高速化が期待できる.
ドライバはNVIDIA公式サイトである https://www.nvidia.co.jp/Download/index.aspx?lang=jp からダウンロードできる.このサイトからダウンロードするときには,グラフィックスカードとオペレーティングシステムを選択する. なお,NVIDIA GeForce Experiance を用いてインストールすることも可能である.
【サイト内の関連ページ】
- NVIDIA グラフィックス・ボードの確認
Windows で,NVIDIA グラフィックス・ボードの種類を調べたいときは, 次のコマンドを実行することにより調べることができる.
wmic path win32_VideoController get name
- NVIDIA ドライバのダウンロード
NVIDIA ドライバは,以下の NVIDIA 公式サイトからダウンロードできる.
- ダウンロードの際には,使用しているグラフィックス・ボードの型番とオペレーティングシステムを選択する.
NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8 のインストール(Windows 上)
NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストール時の注意点
NVIDIAのGPUを使用して並列計算を行うためのツールセット
主な機能: GPU を利用した並列処理,GPU のメモリ管理,C++をベースとした拡張言語とAPIとライブラリ
【NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットの動作に必要なもの】
- CUDA対応のNVIDIA GPUが必要.
そのために,NVIDIA グラフィックス・ボードを確認する. Windows で,NVIDIA グラフィックス・ボードの種類を調べたいときは, 次のコマンドを実行することにより調べることができる.
wmic path win32_VideoController get name
- NVIDIA ドライバのダウンロードとインストール
NVIDIA ドライバは,以下の NVIDIA 公式サイトからダウンロードできる. ダウンロードの際には,使用しているグラフィックス・ボードの型番とオペレーティングシステムを選択する.
- Windows では,インストール前に,Build Tools for Visual Studio もしくは Visual Studio をインストールしておくことが必要である.
【Windows でインストールするときの注意点】
- Windows では, NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストール中は,なるべく他のウインドウはすべて閉じておくこと.
- NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストールが終わったら,ユーザ環境変数 TEMP の設定を行う.
Windows のユーザ名が日本語のとき,nvcc がうまく動作しないエラーを回避するためである.
ユーザ環境変数 TEMP に「C:\TEMP」を設定するために, コマンドプロンプトで,次のコマンドを実行する.
mkdir C:\TEMP powershell -command "[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(\"TEMP\", \"C:\TEMP\", \"User\")"
【関連する外部ページ】
- NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのアーカイブの公式ページ: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive
- NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット の公式のドキュメント: https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-installation-guide-linux/index.html
- NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストールに関する,NVIDIA CUDA クイックスタートガイドの公式ページ: https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-quick-start-guide/index.html
【関連項目】 NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット, NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 12.6 のインストール(Windows 上), NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8 のインストール(Windows 上)
- Windows では,NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストール中は,なるべく他のウインドウはすべて閉じておくこと.
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - 次のコマンドを実行
次のコマンドは,NVIDIA GeForce Experience,NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8 をインストールするものである.
wmic path win32_VideoController get name winget install --scope machine Nvidia.CUDA --version 11.8 powershell -command "[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(\"CUDA_HOME\", \"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.8\", \"Machine\")"
- NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストールが終わったら,ユーザ環境変数 TEMP の設定を行う.
Windows のユーザ名が日本語のとき,nvcc がうまく動作しないエラーを回避するためである.
ユーザ環境変数 TEMP に「C:\TEMP」を設定するために, コマンドプロンプトで,次のコマンドを実行する.
mkdir C:\TEMP powershell -command "[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(\"TEMP\", \"C:\TEMP\", \"User\")"
PyTorch のインストール(Windows 上)
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - 使用する Python のバージョンの確認
python --version
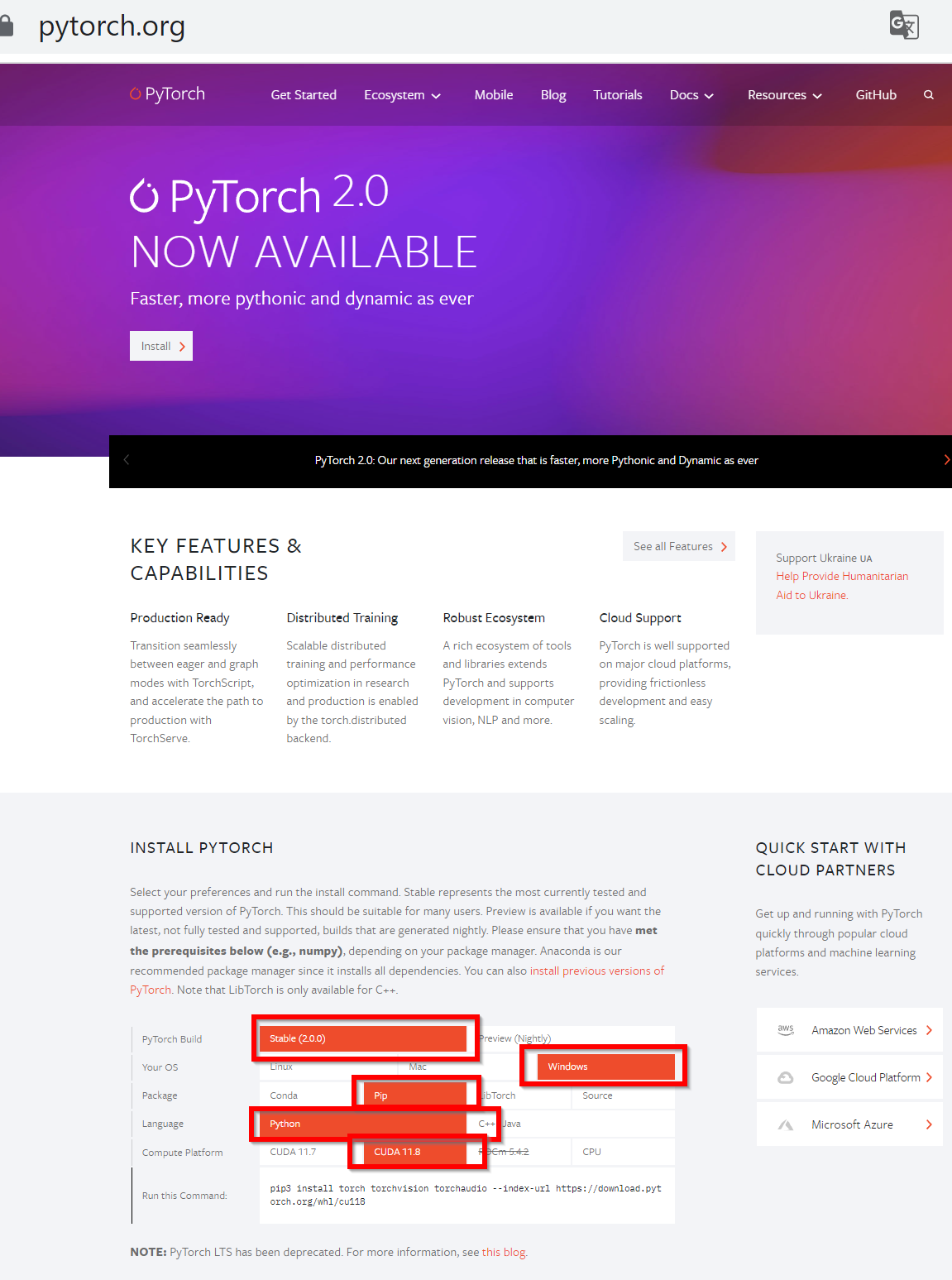
- PyTorch の Web ページを開く
- ランタイムコマンドを表示させる
次のように選ぶと,その下に,ランタイムコマンドが表示される
- Your OS: Windows を選ぶ
- Package: pip を選ぶ
- Language: Python を選ぶ
- CUDA: 使用している CUDA のバージョンを選ぶ
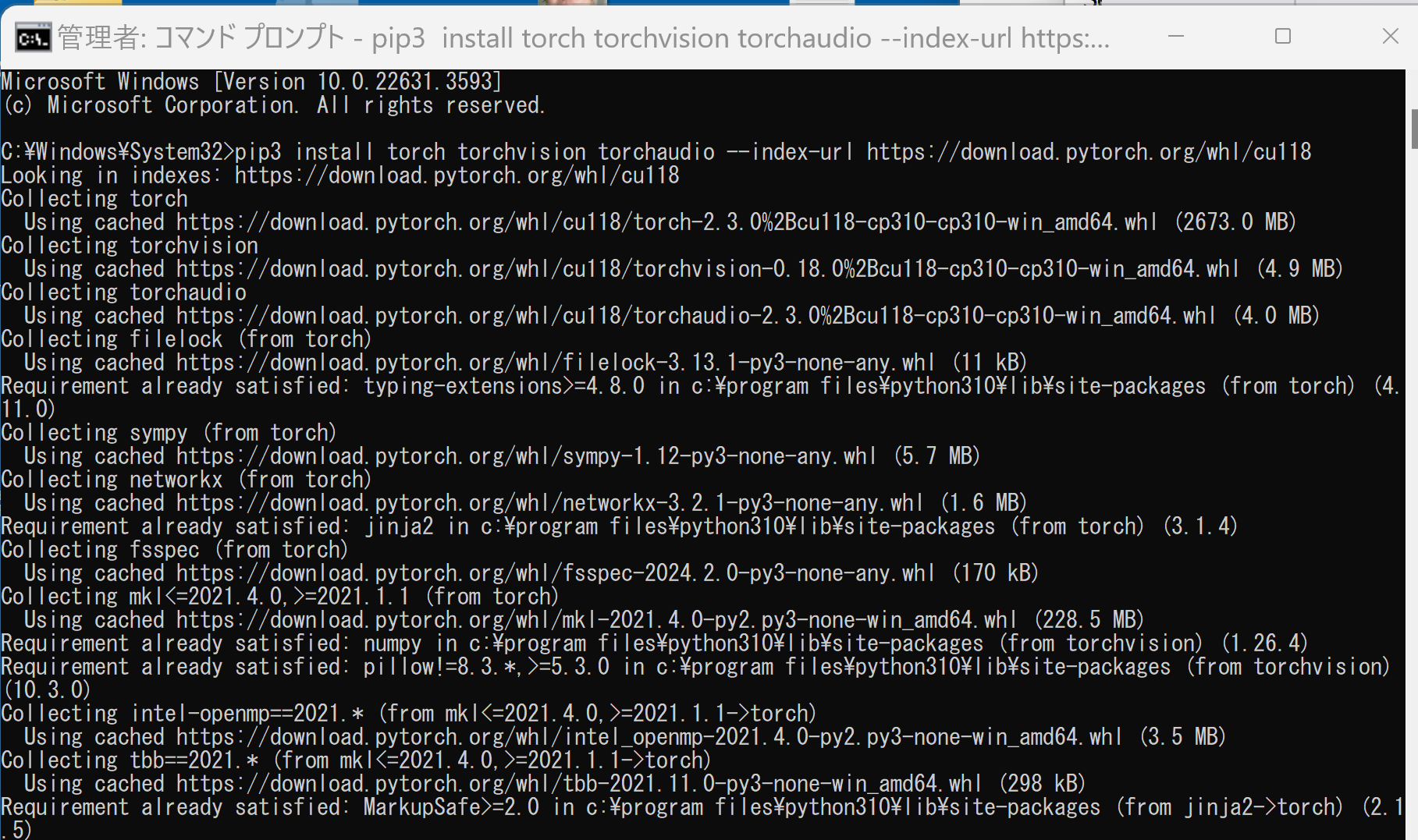
- ランタイムコマンドを,先ほどのコマンドプロンプト(管理者として実行したもの)で実行
PyTorch 2.3 のインストール手順例は次の通り
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - PyTorch のページを確認
- 次のようなコマンドを実行(実行するコマンドは,PyTorch のページの表示されるコマンドを使う).
次のコマンドを実行することにより, PyTorch 2.3 (NVIDIA CUDA 11.8 用)がインストールされる. 但し,Anaconda3を使いたい場合には別手順になる.
事前に NVIDIA CUDA のバージョンを確認しておくこと(ここでは,NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8 が前もってインストール済みであるとする).
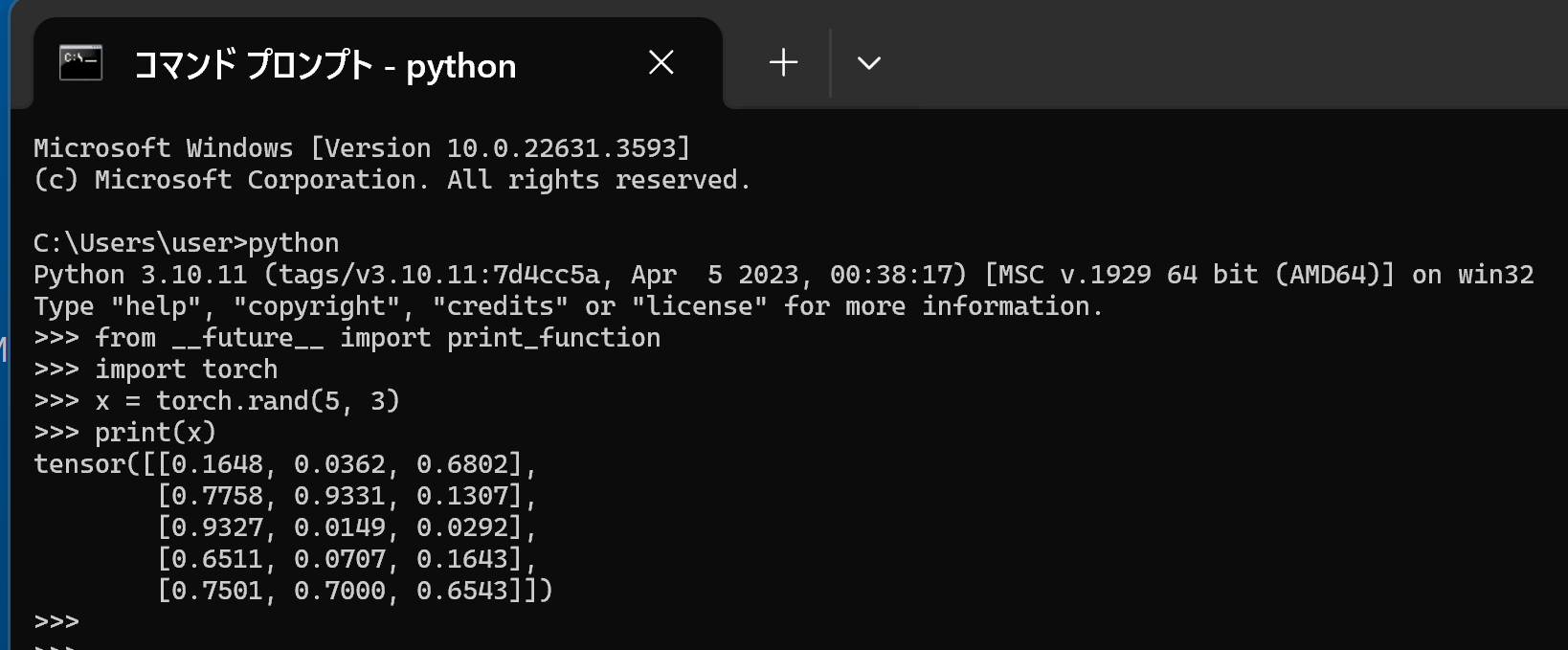
PyTorch で,GPU が動作している場合には,「torch.cuda.is_available()」により,True が表示される.
python -m pip install -U --ignore-installed pip python -m pip uninstall -y torch torchvision torchaudio torchtext xformers python -m pip install -U torch torchvision torchaudio numpy --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118 python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__, torch.cuda.is_available())"
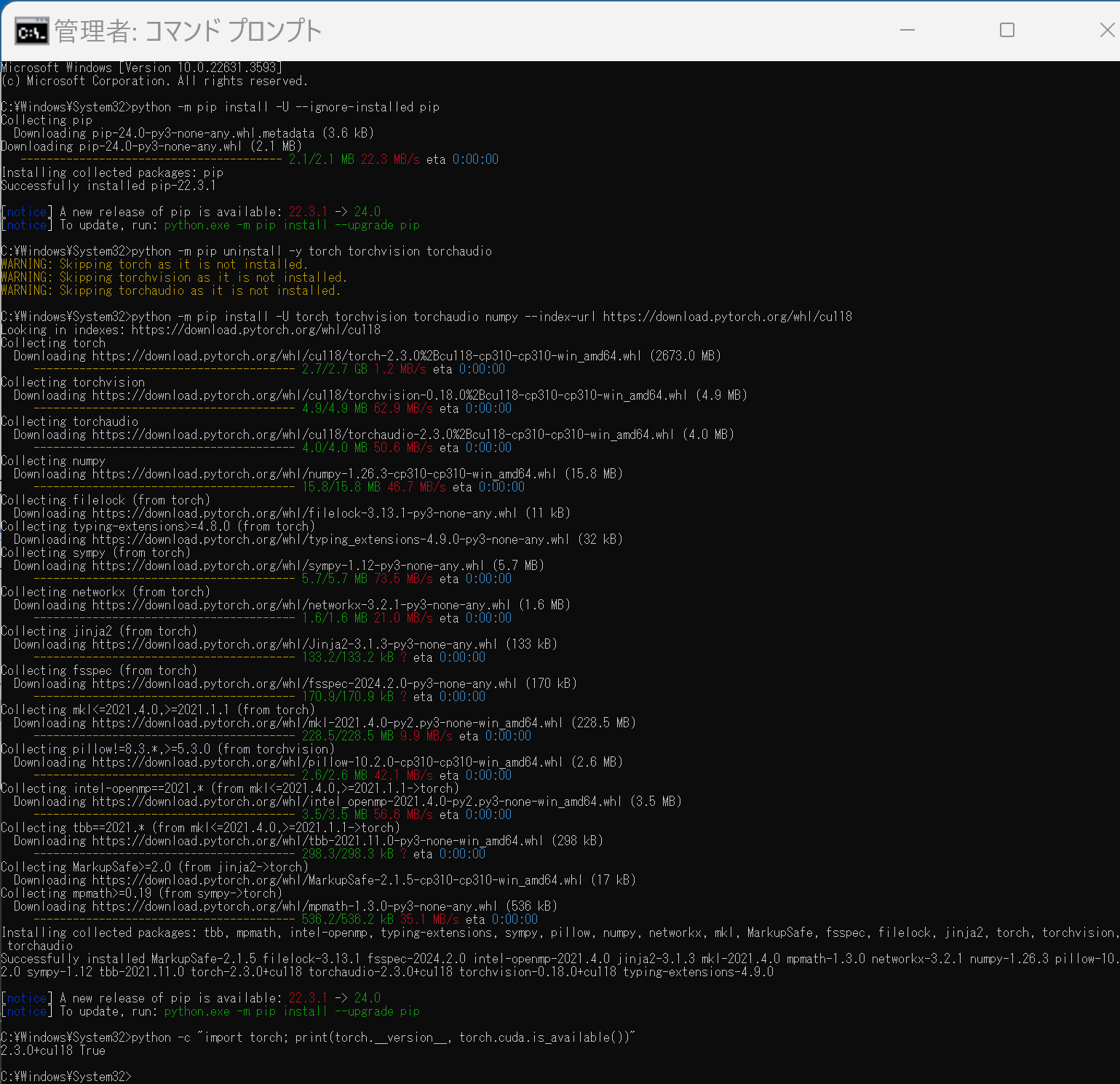
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
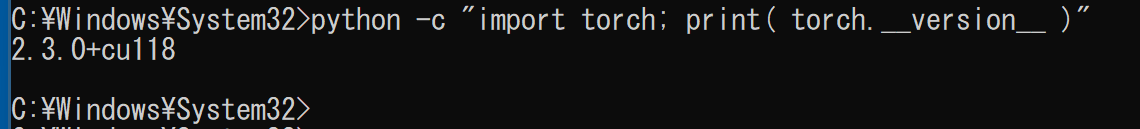
- Python でPyTorch のバージョン確認
python -c "import torch; print( torch.__version__ )"
- 動作確認
https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/ に記載の Python プログラムを動かしてみる
行列の掛け算,主成分分析,特異値分解(PyTorch のプログラム例)(Windows 上)
行列の掛け算
- Windows で,コマンドプロンプトを実行
- エディタを起動
cd /d c:%HOMEPATH% notepad pytorchmul.py
- エディタで,次のプログラムを保存
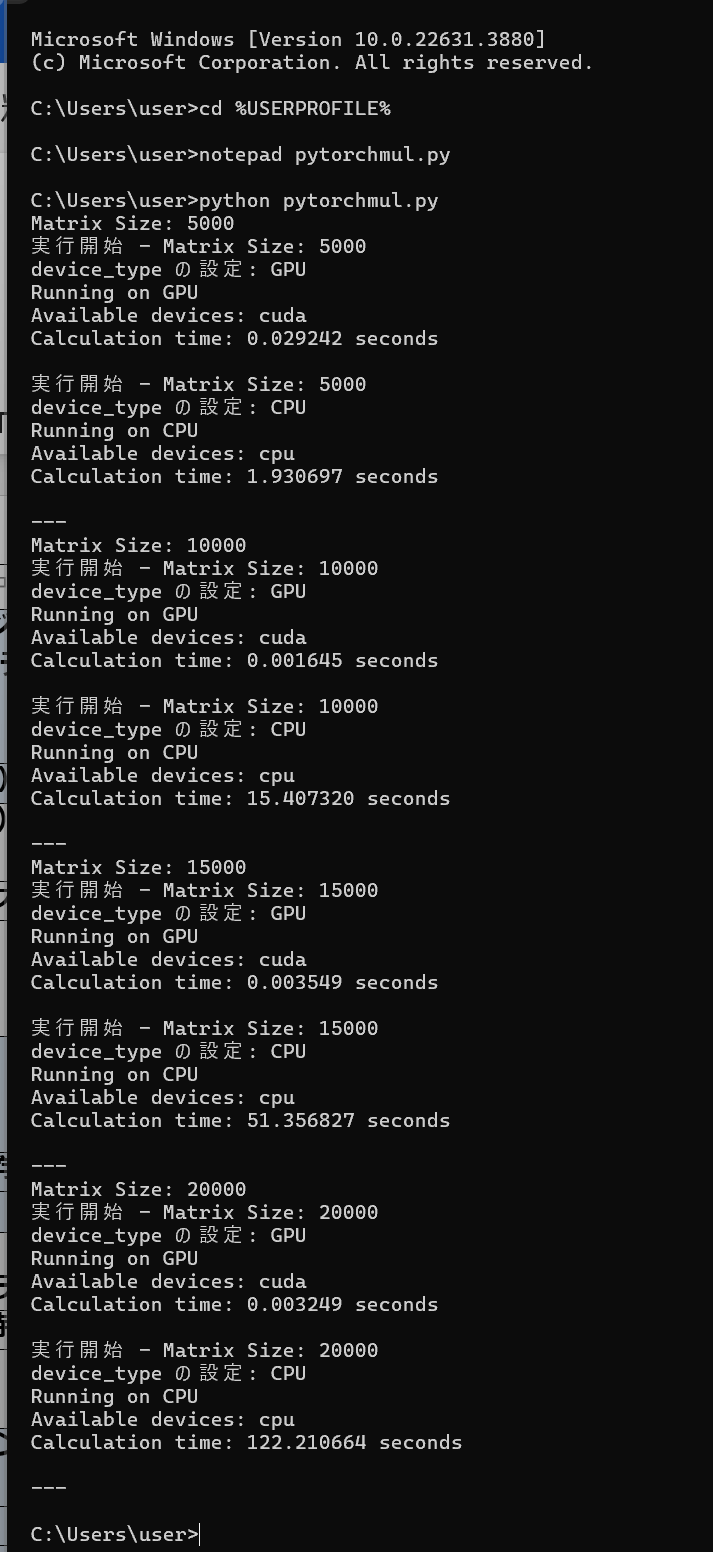
このプログラムは,PyTorch を使用して GPU と CPU での行列積の性能を比較する.異なるサイズ (5000x5000, 10000x10000, 15000x15000, 20000x20000) で,ランダムな値を持つ2つの行列を生成し,それらの行列積を計算する.GPU と CPU それぞれで,行列積の計算時間を測定し,結果を出力する.このことで,GPU と CPU での行列積の性能を比較できる.
import os import torch import time def measure_time(func): start_time = time.perf_counter() result = func() end_time = time.perf_counter() calculation_time = end_time - start_time return calculation_time def run_matmul(device_type, matrix_size): print(f'実行開始 - Matrix Size: {matrix_size}') print('device_type の設定:', device_type) if device_type == 'GPU' and not torch.cuda.is_available(): print("CUDA is not available. Skipping GPU computation.") return device = torch.device('cuda' if device_type == 'GPU' else 'cpu') X = torch.rand(matrix_size, matrix_size, device=device) Y = torch.rand(matrix_size, matrix_size, device=device) def matmul_operation(): return torch.matmul(X, Y) calculation_time = measure_time(matmul_operation) print(f"Running on {device_type}") print(f"Available devices: {device}") print(f"Calculation time: {calculation_time:.6f} seconds") print() def main(): matrix_sizes = [5000, 10000, 15000, 20000] for size in matrix_sizes: print(f'Matrix Size: {size}') run_matmul('GPU', size) run_matmul('CPU', size) print('---') if __name__ == '__main__': main() - Python プログラムの実行
プログラムを pytorchmul.pyのようなファイル名で保存したので, 「python pytorchmul.py」のようなコマンドで行う.
python pytorchmul.py
- 結果の確認
行列積の計算時間が表示される.
主成分分析,特異値分解
- Windows で,コマンドプロンプトを実行
- エディタを起動
cd /d c:%HOMEPATH% notepad pypcasvd.py
- エディタで,次のプログラムを保存
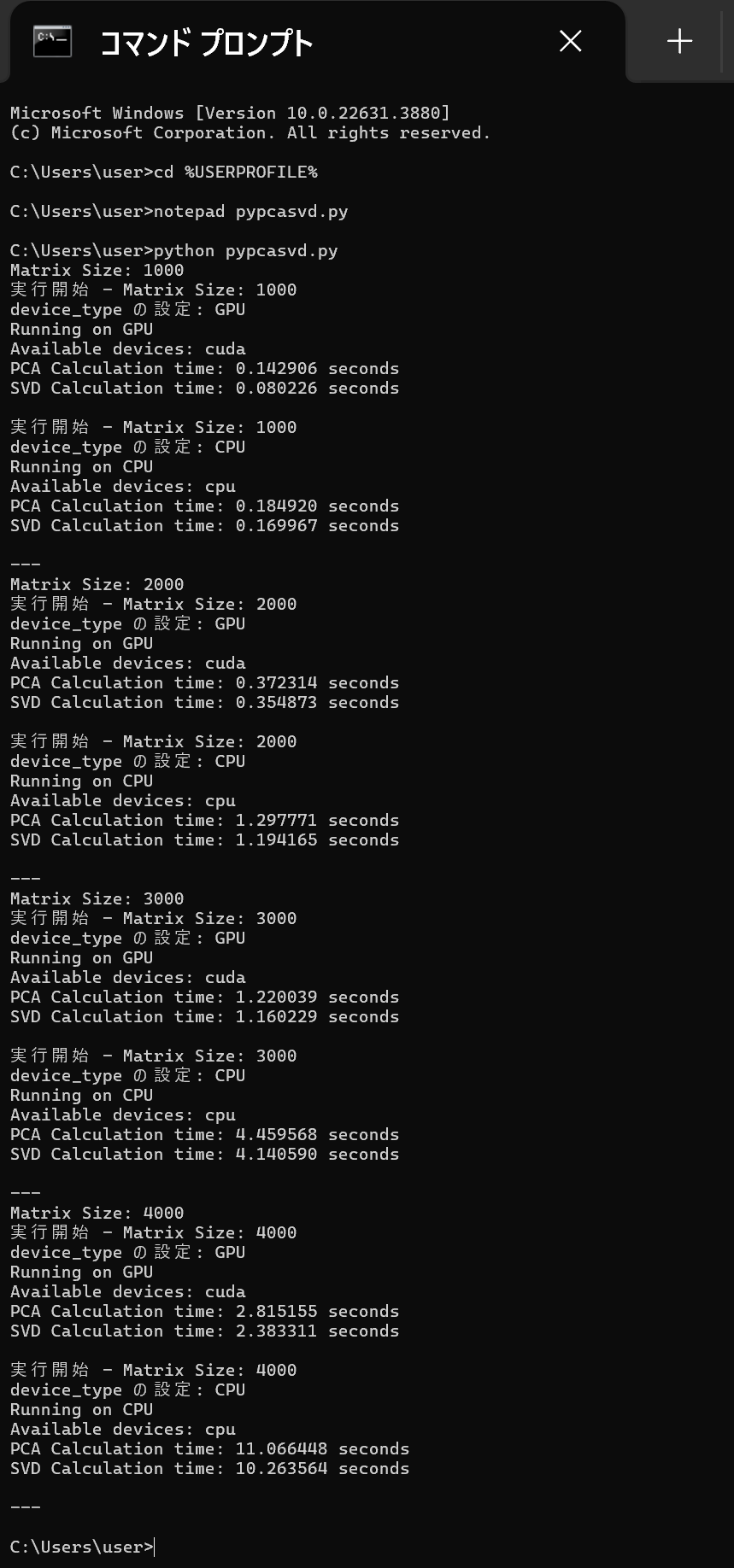
このプログラムは,PyTorch を使用して,行列に対してPCA(主成分分析)とSVD(特異値分解)の計算を行い,GPUとCPUでの実行時間を比較する. [1000, 2000, 3000, 4000] の異なる4通りのサイズの行列に対して, PCAとSVDの計算時間を測定し,結果を表示することで,GPUとCPUの性能の違いを確認できる.
import os import torch import time def measure_time(func): start_time = time.perf_counter() result = func() end_time = time.perf_counter() calculation_time = end_time - start_time return calculation_time def run_pca_svd(device_type, matrix_size): print(f'実行開始 - Matrix Size: {matrix_size}') print('device_type の設定:', device_type) if device_type == 'GPU' and not torch.cuda.is_available(): print("CUDA is not available. Skipping GPU computation.") return device = torch.device('cuda' if device_type == 'GPU' else 'cpu') X = torch.randn(matrix_size, matrix_size, device=device) def pca_operation(): mean = torch.mean(X, dim=0) X_centered = X - mean cov_matrix = torch.matmul(X_centered.T, X_centered) / (matrix_size - 1) _, _, _ = torch.svd(cov_matrix) return None def svd_operation(): _, _, _ = torch.svd(X) return None pca_time = measure_time(pca_operation) svd_time = measure_time(svd_operation) print(f"Running on {device_type}") print(f"Available devices: {device}") print(f"PCA Calculation time: {pca_time:.6f} seconds") print(f"SVD Calculation time: {svd_time:.6f} seconds") print() def main(): matrix_sizes = [1000, 2000, 3000, 4000] for size in matrix_sizes: print(f'Matrix Size: {size}') run_pca_svd('GPU', size) run_pca_svd('CPU', size) print('---') if __name__ == '__main__': main()
- Python プログラムの実行
プログラムを pypcasvd.pyのようなファイル名で保存したので, 「python pypcasvd.py」のようなコマンドで行う.
python pypcasvd.py
- 結果の確認
ImageNet で学習済みの ConvNeXtBase モデルを用いた画像分類(PyTorch, Keras を使用)
ImageNet で学習済みの ConvNeXtBase モデルを用いた画像分類を行う.
- パソコン接続のカメラを使用するので準備しておく
- 前準備として Python 用 opencv-python のインストール
python -m pip install -U opencv-python opencv-contrib-python
- Windows で,コマンドプロンプトを実行
- エディタを起動
cd /d c:%HOMEPATH% notepad pyconvnext.py
- エディタで,次のプログラムを保存
このプログラムは、PyTorchとImageNetで学習済みのConvNeXtBaseモデルを活用し、カメラから取得した画像をリアルタイムで分類します。プログラムでは、GPUの設定、モデルのロード、フレームの前処理、画像分類、結果と推論に要した時間の表示を行います。カメラからの画像をリアルタイムで分類し、その結果をビジュアルに確認できるプログラムです。
【説明】
- set_gpu_config()関数により、GPUの設定を行います。GPUが利用可能な場合は、使用するGPUのデバイス名を表示します。GPUが利用できない場合は、CPUを使用することを表示します。
- preprocess_image()関数により、入力画像の前処理を行います。前処理では、画像のリサイズ、テンソルへの変換、正規化を行います。
- load_model()関数により、ImageNetで学習済みのConvNeXtBaseモデルをロードします。
- classify_camera_frames()関数で、カメラからの画像を取得し、画像分類を行います。
- 取得した画像をpreprocess_image()関数で前処理します。
- 前処理された画像をモデルに入力し、分類を行います。
- 分類結果から、最も確率の高いクラスのラベルと信頼度を取得します。
- 結果(クラスラベル、信頼度、推論時間、フレームレート)を画面上に描画します。
- main()関数で、GPUの設定を行い、モデルをロードし、classify_camera_frames()関数を呼び出してカメラからの画像の分類を開始します。
- 'q'キーが押されるまで、上記の処理を繰り返し行います。'q'キーが押されたら、プログラムを終了します。
【使い方】
- 必要な準備
プログラムを実行する前に、必要なライブラリ(PyTorch、torchvision、OpenCV、urllib)がインストールされていることを確認してください。
- カメラの設定
プログラムはデフォルトでカメラデバイス0を使用します。 異なるカメラを使用する場合は、cv2.VideoCapture(0)の引数を適切なデバイスIDに変更してください。
- モデルの選択
プログラムはデフォルトでconvnext_baseモデルを使用します。 異なるPyTorchのモデルを使用したい場合は、MODEL_NAMEの値を変更してください。 モデルによって入力サイズや前処理の要件が異なる場合があるため、注意が必要です。
- 前処理のパラメータ
プログラムはデフォルトでMEANとSTDの値を使用して前処理を行います。 これらの値は、ImageNetデータセットで使用される一般的な値です。 モデルによっては別の値が適切な場合があります。
- GPUの使用
プログラムは、利用可能な場合はGPUを使用します。 GPUが利用可能でない場合は、自動的にCPUにフォールバックします。
- プログラムの実行
プログラムを実行すると、カメラからのリアルタイム画像分類が開始されます。 分類結果、信頼度、推論時間、フレームレートが画面上に表示されます。
- キー操作:
'q'キーを押すとプログラムが終了します。 'p'キーを押すと、画像の分類を一時停止/再開できます。
- プログラムの終了:
'q'キーを押すか、ウィンドウを閉じるとプログラムが終了します。
以上の手順に従って、プログラムを実行してください。カメラからのリアルタイム画像分類を体験できます。
import torch import torchvision.models as models import torchvision.transforms as transforms import cv2 import json import time import os import numpy as np import urllib.request # ==== 設定 ==== MODEL_NAME = 'convnext_base' MEAN = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406] STD = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225] FPS_BUFFER_SIZE = 10 IMAGENET_LABELS_URL = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/anishathalye/imagenet-simple-labels/master/imagenet-simple-labels.json' # ============= def download_imagenet_labels(url: str, filename: str) -> None: if not os.path.exists(filename): print(f"Downloading {filename} from {url}") try: urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename) print(f"Downloaded {filename}") except Exception as e: print(f"Error downloading {filename}: {str(e)}") raise else: print(f"{filename} already exists.") # ImageNetのクラスラベルとクラス名のマッピングをダウンロード try: download_imagenet_labels(IMAGENET_LABELS_URL, 'imagenet_class_index.json') except Exception as e: print(f"Error downloading imagenet_class_index.json: {str(e)}") exit(1) # ImageNetのクラスラベルとクラス名のマッピングを読み込み try: with open('imagenet_class_index.json', 'r') as f: imagenet_labels = json.load(f) except Exception as e: print(f"Error loading imagenet_class_index.json: {str(e)}") exit(1) def load_model(model_name: str, device: torch.device) -> torch.nn.Module: try: model = getattr(models, model_name)(pretrained=True) model.eval() model.to(device) return model except Exception as e: print(f"Error loading model {model_name}: {str(e)}") raise def get_pretrained_dataset(model: torch.nn.Module) -> str: if hasattr(model, 'default_cfg') and 'url' in model.default_cfg: url = model.default_cfg['url'] if 'imagenet' in url.lower(): return 'ImageNet' else: # urlから推定されるデータセットを返す if 'cifar10' in url.lower(): return 'CIFAR-10' elif 'cifar100' in url.lower(): return 'CIFAR-100' elif 'coco' in url.lower(): return 'COCO' # 他のデータセットに対する条件を追加することができる else: return f'Unknown dataset from url: {url}' return 'Unknown' def get_input_size(model: torch.nn.Module) -> tuple[int, int]: if hasattr(model, 'default_cfg') and 'input_size' in model.default_cfg: return model.default_cfg['input_size'] return (224, 224) # デフォルトの入力サイズ def get_transform(input_size: tuple[int, int], mean: list[float], std: list[float]) -> transforms.Compose: return transforms.Compose([ transforms.ToPILImage(), transforms.Resize(input_size), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean=mean, std=std) ]) def print_model_info(model: torch.nn.Module) -> None: num_classes = model.classifier[2].out_features pretrained_dataset = get_pretrained_dataset(model) input_size = get_input_size(model) print(f"Model: {MODEL_NAME}") print(f"Pretrained dataset: {pretrained_dataset}") print(f"Input image size: {input_size}") print(f"Number of classes: {num_classes}") def preprocess_image(img: np.ndarray, transform: transforms.Compose) -> torch.Tensor: img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) img = transform(img) img = img.unsqueeze(0) return img def classify_image(model: torch.nn.Module, img: torch.Tensor, device: torch.device) -> tuple[str, float]: with torch.no_grad(): img = img.to(device) outputs = model(img) _, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1) class_id = preds.item() class_name = imagenet_labels[class_id] confidence = torch.softmax(outputs, dim=1)[0, preds].item() return class_name, confidence def update_fps(fps_buffer: list[float], prediction_time: float) -> float: fps_buffer.append(prediction_time) if len(fps_buffer) > FPS_BUFFER_SIZE: fps_buffer = fps_buffer[-FPS_BUFFER_SIZE:] fps = len(fps_buffer) / sum(fps_buffer) return fps def display_results(frame: np.ndarray, class_name: str, confidence: float, prediction_time: float, fps: float) -> None: cv2.putText(frame, f"Class: {class_name}", (10, 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.9, (0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.putText(frame, f"Confidence: {confidence:.4f}", (10, 70), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.9, (0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.putText(frame, f"Time: {prediction_time:.4f} seconds", (10, 110), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.9, (0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.putText(frame, f"FPS: {fps:.2f}", (10, 150), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.9, (0, 255, 0), 2) def classify_camera_frames(model: torch.nn.Module, device: torch.device) -> None: input_size = get_input_size(model) transform = get_transform(input_size, MEAN, STD) cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) if not cap.isOpened(): print("Error opening camera") exit(1) fps_buffer = [] paused = False while cap.isOpened(): if not paused: ret, frame = cap.read() if not ret: print("Error reading frame from camera") break img = preprocess_image(frame, transform) start_time = time.perf_counter() class_name, confidence = classify_image(model, img, device) prediction_time = time.perf_counter() - start_time fps = update_fps(fps_buffer, prediction_time) display_results(frame, class_name, confidence, prediction_time, fps) cv2.imshow("Camera Classification", frame) key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF if key == ord('q'): break elif key == ord('p'): paused = not paused cap.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows() def main(): device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') print(f"Using device: {device}") try: model = load_model(MODEL_NAME, device) print_model_info(model) classify_camera_frames(model, device) except Exception as e: print(f"Error in main: {str(e)}") exit(1) if __name__ == '__main__': main() - Python プログラムの実行
プログラムを pyconvnext.pyのようなファイル名で保存したので, 「python pyconvnext.py」のようなコマンドで行う.
python pyconvnext.py
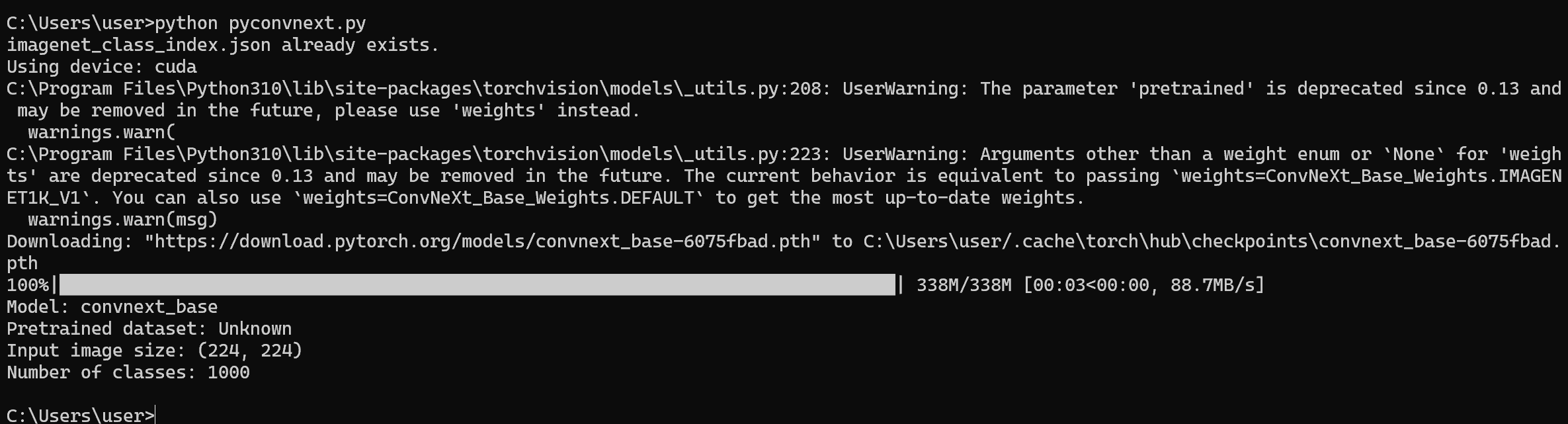
- 結果の確認
終了は q キー

【まとめ】 WindowsでのPyTorch 2.3のインストールのインストールから,GPUとCPUの性能比較,高度な画像分類タスクまでの一連のプロセスを説明.
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)