LCNNによる消失点推定
LCNN
概要
LCNNは、建築物や室内の画像から線分と接合点を検出し、構造的な線画(wireframe)を抽出することを目的とした深層学習モデルである。論文「End-to-End Wireframe Parsing」では、従来手法より高精度な線分検出と接合点検出を実現している。
主要機能
LCNNの主要機能は以下の通りである:
- 線分検出(Line Segment Detection)
- 接合点検出(Junction Detection)
- 構造化された線画解析(Wireframe Parsing)
論文情報
論文タイトル: End-to-End Wireframe Parsing(2019年)
著者: Yichao Zhou, Haozhi Qi, Yi Ma
発表: ICCV 2019
arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.03246
技術的特徴
アーキテクチャ構成
LCNNは以下のモジュールで構成される:
- バックボーン: Stacked Hourglass Network
- Junction Proposal Module (JPM): 接合点(交点)の検出
- Line Sample Module (LSM): 線分のサンプリング
- Line Verification Module (LVM): 線分の検証
主要な技術的貢献
- 線分検出を端点ペアの組み合わせ問題として定式化
- 接合点検出と線分検出を統合的に学習
- 従来手法(LSD、Hough変換)より高精度な検出性能
GitHubリポジトリ
リポジトリURL: https://github.com/zhou13/lcnn
主要ファイル構成
- demo.py: 単一画像での推論デモ
- process.py: 複数画像のバッチ処理
- eval-*.py: 評価スクリプト群
- config/wireframe.yaml: 学習設定ファイル
- lcnn/models/: モデル実装
学習済みモデル
- HuggingFace Repoでの配布(312k iterationsで学習)
- Wireframeデータセットで学習済み
実装手順
- 環境構築
推論の基本的な流れ
- 画像の前処理(正規化、リサイズ)
- モデルによる推論(junction, line maps)
- 後処理(NMS、線分の復元)
- 結果の可視化
カスタマイズのポイント
- config/wireframe.yamlで検出閾値の調整
- 出力される線分情報を消失点推定アルゴリズムに接続
- バッチ処理時はprocess.pyをベースに改造
消失点推定への応用
消失点推定との関係
LCNNの出力(高品質な線分)は消失点推定の入力として利用可能である。ただし、LCNN自体は消失点を直接推定しない。
応用フロー
- LCNN: 画像 → 線分・接合点検出
- 後処理: 検出された線分 → 消失点推定(別途アルゴリズムが必要)
消失点推定の実装方法
LCNNで検出された線分情報から消失点を推定する方法:
- 線分のグループ化: 検出された線分を方向別にクラスタリング
- RANSACによる消失点推定: 各グループ内で交点を計算
- Manhattan World仮定: 3つの主要な消失点を抽出
実装上の利点
- 高品質な線分検出により、ノイズの少ない消失点推定が可能
- 接合点情報を活用した構造的な制約の導入が可能
モデルロードの要件
process_with_lcnn関数で「LCNNモデルを正しくロード」するには、以下の要素が必要である:
- LCNNライブラリ自体のインストール
- モデルアーキテクチャの正しい構築
- チェックポイントの適切なロード
- 前処理・後処理の実装
評価
このモデルは建築物や室内シーンの構造解析において、従来手法より優れた性能を示しており、消失点推定タスクへの応用に適していると評価できる。
LCNN消失点検出プログラム
1. 概要
主要技術名
LCNN(Line Convolutional Neural Network)
論文情報
論文名称:End-to-End Wireframe Parsing
著者:Yichao Zhou, Haozhi Qi, Yi Ma
出典:ICCV 2019
arXiv:https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.03246
技術の新規性・特徴と特徴を活かせるアプリ例
LCNNは、建築物や室内の画像から線分と接合点を検出し、構造的な線画(wireframe)を抽出する深層学習モデルである。従来の線分検出手法(LSD、Hough変換)と異なり、線分検出を端点ペアの組み合わせ問題として定式化し、接合点検出と線分検出を統合的に学習する。これにより高精度な構造解析が可能となる。建築図面の自動解析、室内レイアウト認識、拡張現実における平面検出、ロボットナビゲーションにおける環境理解などに応用できる。
技術を実際に実行して学ぶ体験価値
リアルタイムWebカメラ映像から線分を検出し、消失点を推定する過程を通じて、深層学習による構造解析の実際の動作を体験できる。Manhattan World仮定やRANSACアルゴリズムの組み合わせによる頑健な推定手法を学習し、AIがどのように画像内の幾何学的構造を抽出し、空間の遠近感を自動的に認識するかを理解できる。
2. 事前準備
Python, Windsurfをインストールしていない場合の手順(インストール済みの場合は実行不要)。
- 管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動する(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。
- 以下のコマンドをそれぞれ実行する(winget コマンドは1つずつ実行)。
REM Python をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 -e --silent
REM Windsurf をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Codeium.Windsurf -e --silent
REM Python のパス設定
set "PYTHON_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312"
set "PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312\Scripts"
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_PATH%" /M >nul
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" /M >nul
REM Windsurf のパス設定
set "WINDSURF_PATH=C:\Program Files\Windsurf"
if exist "%WINDSURF_PATH%" (
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%WINDSURF_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%WINDSURF_PATH%" /M >nul
)LCNNリポジトリと依存パッケージのインストール
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。
winget install --scope machine --id Git.Git -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements
REM Git のパス設定
set "NEW_PATH=C:\Program Files\Git\cmd"
if exist "%NEW_PATH%" echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%NEW_PATH%" >nul
if exist "%NEW_PATH%" if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%NEW_PATH%" /M >nul新しいコマンドプロンプトを開き、以下を実行する。
pip install -U torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126
pip install opencv-python matplotlib scipy scikit-image scikit-learn tensorboard tensorboardX huggingface-hub
# リポジトリをクローン
cd %USERPROFILE%\Documents
git clone https://github.com/zhou13/lcnn.git学習済みモデルの準備
LCNNのGitHubリポジトリの指示に従い、学習済みモデル(190418-201834-f8934c6-lr4d10-312k.pth)をHuggingFaceからダウンロードし、`%USERPROFILE%\Documents\lcnn\pretrained\Pretrained\`フォルダに配置する。
3. プログラムコード
# LCNN消失点検出プログラム
# リアルタイムWebカメラ入力による線分検出と消失点推定
# 論文: "End-to-End Wireframe Parsing" (ICCV 2019)
# GitHub: https://github.com/zhou13/lcnn
# 特徴: LCNNは線分と接合点を統合的に推定し,建築物や室内シーンの構造解析に利用できる
# 前準備: pip install torch torchvision opencv-python scikit-image scikit-learn pillow
# cd %USERPROFILE%\Documents
# git clone https://github.com/zhou13/lcnn.git
# 設計方針:
# • 計算および描画はキャンバス座標系(512×512)で統一する
# • LCNN出力のH["lines"]は(y,x)形式で出力されるため,消失点計算用に(x,y)形式へ変換する
# • H["lines"] のスケールは値域に基づいて自動判定し,{1, 128, 256, 512} の候補に
# 1.2倍のマージンでスナップしてキャンバス座標に変換する
# • 画面上のテキスト描画は Pillow と OpenCV を併用し,フォントは C:/Windows/Fonts/meiryo.ttc を使用する
# • cap.grab() → ret, frame = cap.retrieve() → if not ret: break の取得処理は変更しない
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
import skimage.transform
import sys
import random
import time
from datetime import datetime
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
import urllib.request
# 定数定義
INTERSECTION_THRESHOLD = 1e-10
MIN_LINE_LENGTH = 50
SCORE_THRESHOLD = 0.8
RANSAC_ITERATIONS = 1000
RANSAC_SAMPLE_SIZE = 2
RANSAC_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD = 5.0
MANHATTAN_ANGLE_TOLERANCE = 30.0
HISTOGRAM_BIN_WIDTH = 5.0
ITERATION_MAX_COUNT = 5
CONVERGENCE_THRESHOLD = 1.0
CLUSTER_RANGE = 15.0
RANDOM_SEED = 42
CANVAS_SIZE = 512 # 計算・描画をこの座標系で統一
# プログラム概要と操作方法の表示
print("=" * 60)
print("LCNN消失点検出プログラム")
print("=" * 60)
print("概要:")
print(" 動画/カメラ映像を解析し,線分検出と消失点推定を行う。")
print("")
print("操作方法:")
print(" - 'q'キー: プログラムを終了")
print(" - カメラに直線的な構造物が映るように調整する")
print("")
print("注意事項:")
print(" - 初回実行時はモデルの読み込みに時間がかかる場合がある")
print(" - 消失点はキャンバス座標系で可視化する")
print("=" * 60)
print("")
# LCNNパスを追加
lcnn_path = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser('~'), 'Documents', 'lcnn')
sys.path.insert(0, lcnn_path)
# LCNNライブラリのインポート
import lcnn
from lcnn.config import C, M
from lcnn.models.line_vectorizer import LineVectorizer
from lcnn.models.multitask_learner import MultitaskHead, MultitaskLearner
from lcnn.postprocess import postprocess
# パス設定
config_path = os.path.join(lcnn_path, 'config', 'wireframe.yaml')
checkpoint_path = os.path.join(lcnn_path, 'pretrained', 'Pretrained', '190418-201834-f8934c6-lr4d10-312k.pth')
# GPU/CPU自動選択
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(f'デバイス: {str(device)}')
# GPU使用時の最適化
if device.type == 'cuda':
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
# LCNNモデルをロード
print("モデルを読み込み中...")
C.update(C.from_yaml(filename=config_path))
M.update(C.model)
checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_path, map_location=device)
model = lcnn.models.hg(
depth=M.depth,
head=lambda c_in, c_out: MultitaskHead(c_in, c_out),
num_stacks=M.num_stacks,
num_blocks=M.num_blocks,
num_classes=sum(sum(M.head_size, [])),
)
model = MultitaskLearner(model)
model = LineVectorizer(model)
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint["model_state_dict"])
model = model.to(device)
model.eval()
print("モデルの読み込み完了")
# フォント設定(Pillowで描画)
FONT_PATH = 'C:/Windows/Fonts/meiryo.ttc'
FONT_SIZE = 20
try:
font = ImageFont.truetype(FONT_PATH, FONT_SIZE)
except:
font = ImageFont.load_default()
print("注意: 指定フォントを読み込めなかったため代替フォントを使用する。")
# スケール自動判定ヘルパ(修正版)
def autoscale_lines_to_canvas(lines_yx, canvas_h, canvas_w):
"""
lines_yx: shape (N, 2, 2) with (y,x) order from LCNN
値域を観測し,適切なスケールを判定してキャンバス座標へ変換する
戻り値: (x,y)形式に変換されたキャンバス座標の線分配列
"""
if len(lines_yx) == 0:
return lines_yx
# 全座標の最大値と分布を確認
all_coords = lines_yx.reshape(-1)
vmax = float(np.max(np.abs(all_coords)))
vmean = float(np.mean(np.abs(all_coords)))
# より適切なスケール判定
candidates = [1.0, 128.0, 256.0, 512.0]
base = None
# 平均値も考慮してスケールを判定
for cand in candidates:
if vmax <= cand * 1.5 and vmean <= cand * 0.8:
base = cand
break
if base is None:
base = 512.0 # デフォルトは最大スケール
scale_y = canvas_h / base
scale_x = canvas_w / base
scaled = lines_yx.copy().astype(np.float32)
scaled[:, :, 0] *= scale_y # y座標のスケーリング
scaled[:, :, 1] *= scale_x # x座標のスケーリング
# (y,x)から(x,y)形式に変換
lines_xy = np.zeros_like(scaled)
lines_xy[:, :, 0] = scaled[:, :, 1] # x座標
lines_xy[:, :, 1] = scaled[:, :, 0] # y座標
return lines_xy
# RANSACの初期シード設定(反復外で一度だけ設定)
random.seed(RANDOM_SEED)
# グローバル変数
frame_count = 0
results_log = []
def video_frame_processing(frame):
global frame_count
current_time = time.time()
frame_count += 1
# BGR→RGB変換(OpenCVはBGR,その後の処理はRGB想定)
frame_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# ネットワーク入力用にキャンバスへリサイズ(RGB形式で処理)
im = frame_rgb
if im.ndim == 2:
im = np.repeat(im[:, :, None], 3, 2)
im = im[:, :, :3]
im_resized = skimage.transform.resize(im, (CANVAS_SIZE, CANVAS_SIZE)) * 255.0 # RGB, float
image = (im_resized - M.image.mean) / M.image.stddev
image = torch.from_numpy(np.rollaxis(image, 2)[None].copy()).float()
# 推論実行
with torch.no_grad():
input_dict = {
"image": image.to(device),
"meta": [
{
"junc": torch.zeros(1, 2).to(device),
"jtyp": torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.uint8).to(device),
"Lpos": torch.zeros(2, 2, dtype=torch.uint8).to(device),
"Lneg": torch.zeros(2, 2, dtype=torch.uint8).to(device),
}
],
"target": {
"jmap": torch.zeros([1, 1, 128, 128]).to(device),
"joff": torch.zeros([1, 1, 2, 128, 128]).to(device),
},
"mode": "testing",
}
H = model(input_dict)["preds"]
# LCNN出力((y,x))をキャンバス座標系の(x,y)へ変換
raw_lines = H["lines"][0].cpu().numpy() # (N,2,2) in (y,x)
scores = H["score"][0].cpu().numpy()
lines = autoscale_lines_to_canvas(raw_lines, CANVAS_SIZE, CANVAS_SIZE)
# 重複線分除去(修正版)
if len(lines) > 1:
unique_lines = []
unique_scores = []
for i in range(len(lines)):
is_duplicate = False
for j in range(len(unique_lines)):
# キャンバス座標系に適した許容誤差(5ピクセル程度に拡大)
if np.allclose(lines[i], unique_lines[j], atol=5.0):
is_duplicate = True
break
# 逆順の線分チェック
if lines[i].shape == (2, 2) and unique_lines[j].shape == (2, 2):
reversed_line = np.array([lines[i][1], lines[i][0]])
if np.allclose(reversed_line, unique_lines[j], atol=5.0):
is_duplicate = True
break
if not is_duplicate:
unique_lines.append(lines[i])
unique_scores.append(scores[i])
if len(unique_lines) > 0:
lines = np.array(unique_lines)
scores = np.array(unique_scores)
else:
lines = np.array([])
scores = np.array([])
# 後処理(キャンバス座標系で実施)
if len(lines) > 0:
diag = (CANVAS_SIZE**2 + CANVAS_SIZE**2) ** 0.5
nlines, nscores = postprocess(lines, scores, diag * 0.01, 0, False)
else:
nlines = []
nscores = []
# スコア閾値フィルタ
filtered_lines = []
filtered_scores = []
if len(nlines) > 0 and len(nscores) > 0:
for line, score in zip(nlines, nscores):
if score >= SCORE_THRESHOLD:
filtered_lines.append(line)
filtered_scores.append(score)
# 線分から消失点を検出(既に(x,y)形式)
vanishing_points = []
if len(filtered_lines) >= 2:
height, width = CANVAS_SIZE, CANVAS_SIZE
# 線分の長さフィルタリング(座標系統一済み)
length_filtered_lines = []
length_filtered_scores = []
for line, score in zip(filtered_lines, filtered_scores):
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = line # 既に(x,y)形式
length = np.sqrt((x2 - x1) ** 2 + (y2 - y1) ** 2)
if length >= MIN_LINE_LENGTH:
length_filtered_lines.append([(x1, y1), (x2, y2)])
length_filtered_scores.append(score)
if len(length_filtered_lines) >= 2:
# 段階1: 方向クラスタリング
line_angles = []
for (x1, y1), (x2, y2) in length_filtered_lines:
angle = np.degrees(np.arctan2(y2 - y1, x2 - x1)) % 180.0
line_angles.append(angle)
num_bins = int(180 / HISTOGRAM_BIN_WIDTH)
angle_histogram = np.zeros(num_bins)
for angle in line_angles:
bin_idx = int(angle / HISTOGRAM_BIN_WIDTH)
if 0 <= bin_idx < num_bins:
angle_histogram[bin_idx] += 1
peak_threshold = max(1, int(len(length_filtered_lines) * 0.1))
peak_angles = []
for i in range(len(angle_histogram)):
if angle_histogram[i] >= peak_threshold:
is_peak = True
if i > 0 and angle_histogram[i] < angle_histogram[i - 1]:
is_peak = False
if i < len(angle_histogram) - 1 and angle_histogram[i] < angle_histogram[i + 1]:
is_peak = False
if is_peak:
peak_angles.append(i * HISTOGRAM_BIN_WIDTH)
direction_clusters = []
for peak_angle in peak_angles:
cluster_lines = []
cluster_scores = []
for i, angle in enumerate(line_angles):
angle_diff = min(abs(angle - peak_angle), 180 - abs(angle - peak_angle))
if angle_diff <= CLUSTER_RANGE:
cluster_lines.append(length_filtered_lines[i])
cluster_scores.append(length_filtered_scores[i])
if len(cluster_lines) >= 2:
direction_clusters.append((cluster_lines, cluster_scores, peak_angle))
# 段階2: Manhattan World制約
manhattan_groups = []
if len(direction_clusters) >= 2:
horizontal_clusters = []
vertical_clusters = []
for cluster_lines, cluster_scores, peak_angle in direction_clusters:
if (peak_angle <= MANHATTAN_ANGLE_TOLERANCE or
peak_angle >= 180 - MANHATTAN_ANGLE_TOLERANCE):
horizontal_clusters.append((cluster_lines, cluster_scores, peak_angle))
elif abs(peak_angle - 90) <= MANHATTAN_ANGLE_TOLERANCE:
vertical_clusters.append((cluster_lines, cluster_scores, peak_angle))
else:
manhattan_groups.append(((cluster_lines, cluster_scores, peak_angle), "diagonal"))
if horizontal_clusters:
horizontal_clusters.sort(key=lambda x: len(x[0]), reverse=True)
manhattan_groups.insert(0, (horizontal_clusters[0], "horizontal"))
if vertical_clusters:
vertical_clusters.sort(key=lambda x: len(x[0]), reverse=True)
manhattan_groups.insert(0, (vertical_clusters[0], "vertical"))
if len(manhattan_groups) == 0:
all_lines_group = [(line, score) for line, score in zip(length_filtered_lines, length_filtered_scores)]
if len(all_lines_group) >= 2:
manhattan_groups = [(all_lines_group, "general")]
else:
labeled_groups = []
for item in manhattan_groups:
group_data, label = item if len(item) == 2 else (item[0], item[1])
if isinstance(group_data, tuple) and len(group_data) == 3:
cluster_lines, cluster_scores, _ = group_data
group_data = [(line, score) for line, score in zip(cluster_lines, cluster_scores)]
labeled_groups.append((group_data, label))
manhattan_groups = labeled_groups
# 段階3-5: RANSAC + 重み付き最小二乗 + 反復改善(修正版)
estimated_vps = []
for group_data, _group_type in manhattan_groups:
if len(group_data) >= 2:
group_lines = [item[0] for item in group_data]
group_scores = [item[1] for item in group_data]
# RANSAC(スコア重み付きサンプリング)
best_vp = None
best_support = 0
# スコアによる重み付きサンプリング確率を計算
normalized_scores = np.array(group_scores) / np.sum(group_scores)
for _ in range(RANSAC_ITERATIONS):
if len(group_lines) >= RANSAC_SAMPLE_SIZE:
# スコアに基づく重み付きサンプリング
indices = np.random.choice(len(group_lines), RANSAC_SAMPLE_SIZE,
replace=False, p=normalized_scores)
i1, i2 = indices[0], indices[1]
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = group_lines[i1]
(x3, y3), (x4, y4) = group_lines[i2]
v1 = np.array([x2 - x1, y2 - y1], dtype=np.float64)
v2 = np.array([x4 - x3, y4 - y3], dtype=np.float64)
denom = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0]
if abs(denom) > INTERSECTION_THRESHOLD:
dx = x3 - x1
dy = y3 - y1
t = (dx * v2[1] - dy * v2[0]) / denom
vp_x = x1 + t * v1[0]
vp_y = y1 + t * v1[1]
# 一貫した境界判定
if -width * 2 <= vp_x <= width * 3 and -height * 2 <= vp_y <= height * 3:
support_count = 0
for (tx1, ty1), (tx2, ty2) in group_lines:
line_length = np.hypot(tx2 - tx1, ty2 - ty1)
if line_length > 0:
distance = abs((ty2 - ty1) * vp_x - (tx2 - tx1) * vp_y +
tx2 * ty1 - ty2 * tx1) / line_length
if distance <= RANSAC_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD:
support_count += 1
if support_count > best_support:
best_support = support_count
best_vp = (vp_x, vp_y)
if best_vp is not None and best_support >= 2:
vp_x, vp_y = best_vp
for _ in range(ITERATION_MAX_COUNT):
# 現在の距離計算
current_distances = []
for (x1, y1), (x2, y2) in group_lines:
line_length = np.hypot(x2 - x1, y2 - y1)
if line_length > 0:
distance = abs((y2 - y1) * vp_x - (x2 - x1) * vp_y +
x2 * y1 - y2 * x1) / line_length
current_distances.append(distance)
else:
current_distances.append(float('inf'))
# 重み付き最小二乗
A_matrix = []
b_vector = []
weights = []
for i, ((x1, y1), (x2, y2)) in enumerate(group_lines):
length = np.hypot(x2 - x1, y2 - y1)
confidence = group_scores[i]
distance = current_distances[i]
if length > 0 and distance < float('inf'):
weight = length * confidence / (1 + distance * distance)
a = y2 - y1
b_coeff = x1 - x2
c = x2 * y1 - x1 * y2
norm = np.hypot(a, b_coeff)
if norm > 0:
a /= norm
b_coeff /= norm
c /= norm
A_matrix.append([a, b_coeff])
b_vector.append(-c)
weights.append(weight)
if len(A_matrix) >= 2:
A_matrix = np.array(A_matrix, dtype=np.float64)
b_vector = np.array(b_vector, dtype=np.float64)
weights = np.array(weights, dtype=np.float64) if len(weights) > 0 else np.ones(len(b_vector), dtype=np.float64)
W = np.diag(weights)
AtWA = A_matrix.T @ W @ A_matrix
AtWb = A_matrix.T @ W @ b_vector
# 数値安定性向上:正則化係数を適切に調整
AtWA += 1e-2 * np.eye(2)
# 判定閾値を適切に設定
if np.linalg.det(AtWA) > 1e-6:
solution = np.linalg.solve(AtWA, AtWb)
new_vp_x, new_vp_y = solution
change = np.hypot(new_vp_x - vp_x, new_vp_y - vp_y)
vp_x, vp_y = new_vp_x, new_vp_y
if change < CONVERGENCE_THRESHOLD:
break
estimated_vps.append((vp_x, vp_y, best_support))
# 画像境界の拡張範囲でフィルタ(一貫した判定)
for vp_x, vp_y, support in estimated_vps:
if -width * 2 <= vp_x <= width * 3 and -height * 2 <= vp_y <= height * 3:
vanishing_points.append((int(vp_x), int(vp_y), support))
# 表示用フレーム(RGB形式で作成)
result = np.clip(im_resized, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
# 線分描画(OpenCV用にBGRに変換)
result_bgr = cv2.cvtColor(result, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
for (x1, y1), (x2, y2) in filtered_lines:
cv2.line(result_bgr, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x2), int(y2)), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# OpenCVで確実に見える赤い円を描画
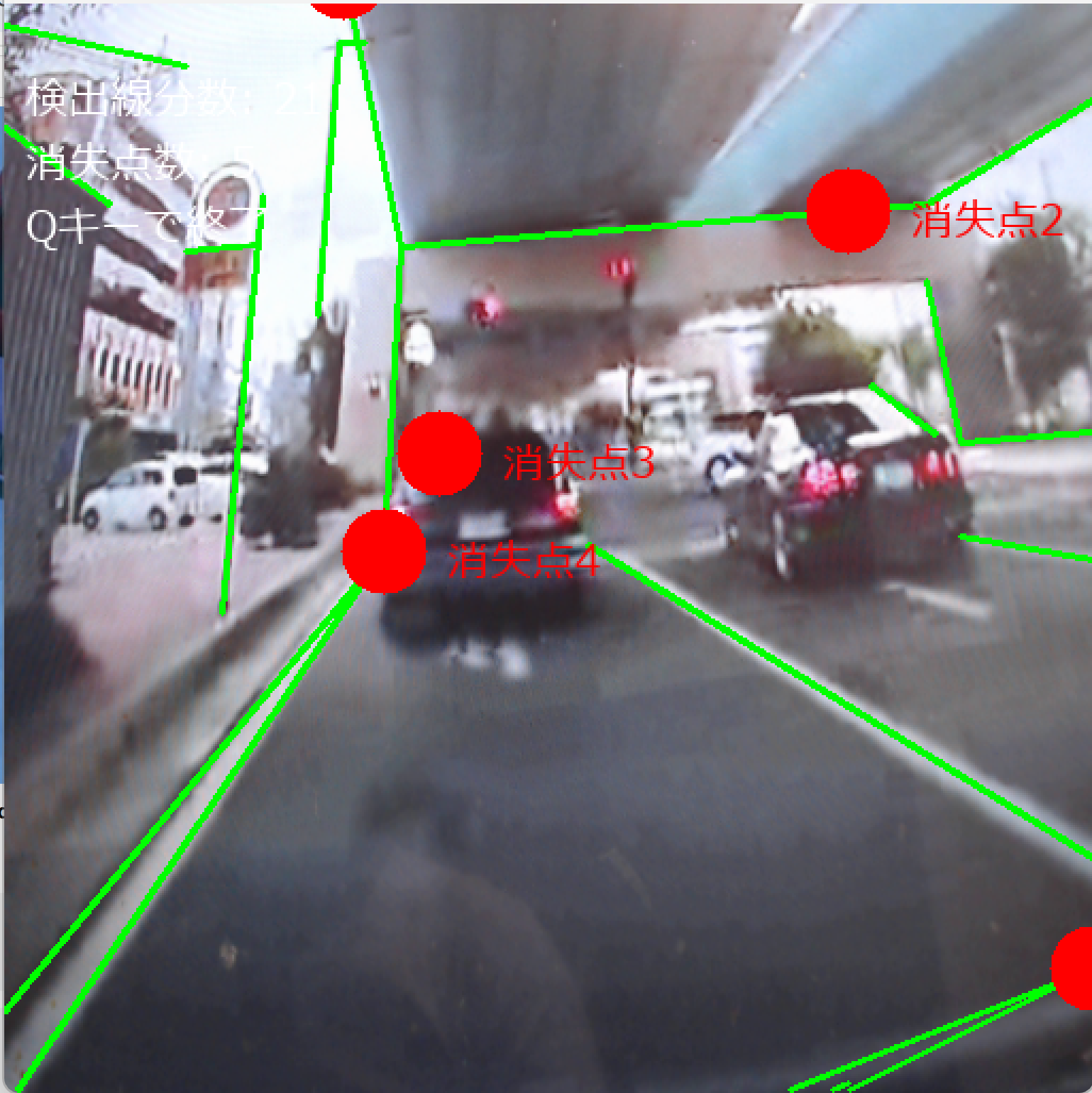
for i, (vp_x, vp_y, _count) in enumerate(vanishing_points):
# 大きな赤い円(半径20)
cv2.circle(result_bgr, (vp_x, vp_y), 20, (0, 0, 255), -1) # 塗りつぶし円のみ
# 消失点テキスト表示(Pillow使用)
img_pil = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(result_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img_pil)
for i, (vp_x, vp_y, _count) in enumerate(vanishing_points):
# テキストはPillowで描画
draw.text((vp_x + 30, vp_y - 10), f'消失点{i+1}', font=font, fill=(255, 0, 0))
# 情報表示
draw.text((10, 30), f'検出線分数: {len(filtered_lines)}', font=font, fill=(255, 255, 255))
draw.text((10, 60), f'消失点数: {len(vanishing_points)}', font=font, fill=(255, 255, 255))
draw.text((10, 90), 'Qキーで終了', font=font, fill=(255, 255, 255))
result_final = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(img_pil), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# 結果文字列の作成
if len(vanishing_points) > 0:
vp_str = ", ".join([f"VP{i+1}:({vp_x},{vp_y})" for i, (vp_x, vp_y, _) in enumerate(vanishing_points)])
else:
vp_str = "消失点なし"
result_str = f"線分:{len(filtered_lines)}, {vp_str}"
return result_final, result_str, current_time
print("0: 動画ファイル")
print("1: カメラ")
print("2: サンプル動画")
choice = input("選択: ")
if choice == '0':
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
path = filedialog.askopenfilename()
if not path:
exit()
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(path)
elif choice == '1':
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0, cv2.CAP_DSHOW)
if not cap.isOpened():
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_BUFFERSIZE, 1)
else:
# サンプル動画ダウンロード・処理
SAMPLE_URL = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/opencv/opencv/master/samples/data/vtest.avi'
SAMPLE_FILE = 'vtest.avi'
urllib.request.urlretrieve(SAMPLE_URL, SAMPLE_FILE)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(SAMPLE_FILE)
if not cap.isOpened():
print('動画ファイル・カメラを開けませんでした')
exit()
# メイン処理
print('\n=== 動画処理開始 ===')
print('操作方法:')
print(' q キー: プログラム終了')
try:
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
MAIN_FUNC_DESC = "LCNN消失点検出"
processed_frame, result, current_time = video_frame_processing(frame)
cv2.imshow(MAIN_FUNC_DESC, processed_frame)
if choice == '1': # カメラの場合
print(datetime.fromtimestamp(current_time).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f")[:-3], result)
else: # 動画ファイルの場合
print(frame_count, result)
results_log.append(result)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
finally:
print('\n=== プログラム終了 ===')
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if results_log:
with open('result.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write('=== 結果 ===\n')
f.write(f'処理フレーム数: {frame_count}\n')
f.write(f'使用デバイス: {str(device).upper()}\n')
if device.type == 'cuda':
f.write(f'GPU: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)}\n')
f.write('\n')
f.write('\n'.join(results_log))
print(f'\n処理結果をresult.txtに保存しました')
4. 使用方法
実行手順
- プログラムファイルを`lcnn_vanishing_point.py`として保存する。
- Webカメラが接続されていることを確認する。
- コマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。
cd %USERPROFILE%\Documents
python lcnn_vanishing_point.py- Webカメラが起動し、リアルタイムで線分検出と消失点推定が実行される。
- 緑色の線が検出された線分、赤色の円が推定された消失点を示す。
- 'q'キーを押すとプログラムが終了する。
動作確認のポイント
建築物や室内の角、直線的な構造物をカメラに向けると、線分が検出され消失点が推定される。Manhattan World仮定に基づく3つの主要な消失点(水平方向2つ、垂直方向1つ)の検出が期待される。
5. 実験・探求のアイデア
AIモデル選択による比較実験
LCNN以外の線分検出手法(OpenCVのHoughLinesP、LSD)との比較実験を実施し、検出精度や処理速度の違いを評価する。config/wireframe.yaml内の設定変更による検出挙動の変化を観察する。
実験要素の調整
プログラム内の定数(SCORE_THRESHOLD、MIN_LINE_LENGTH、RANSAC_ITERATIONS等)を変更し、検出性能への影響を観察する。Manhattan World制約の有無による消失点推定精度の変化を検証する。
体験・実験・探求のアイデア
異なる環境(屋外建築物、室内空間、人工構造物)での検出性能の違いを調査する。カメラの角度や距離を変化させて、消失点推定の安定性を評価する。複数の消失点が同時に検出される条件を探求し、3点透視図法の原理を実際に確認する。検出された線分情報を用いて、建築物の3次元構造推定や平面検出への応用可能性を検討する。静止画入力への改造や処理速度の最適化についても実験し、LCNNの内部動作(Junction Proposal Module、Line Sample Module、Line Verification Module)の理解を深める。
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)