DPT による床面段差検出(ソースコードと実行結果)
プログラム利用ガイド
1. このプログラムの利用シーン
本プログラムは、環境中の床面段差を視覚的に検出・可視化するツールである。主な応用分野として、バリアフリー環境の調査、建築物の安全点検、自律移動ロボットの環境認識などが想定される。
利用に際しては、単眼カメラによる深度推定の限界を理解することが重要である。本プログラムが推定する段差の高さは絶対値ではなく、画像内の相対的な深度情報から導かれた近似値である。したがって、表示される数値は参考値として扱い、正確な測定が必要な場合は別途計測器具を使用することが推奨される。一方で、段差の存在とおおよその位置を迅速に把握する用途には適している。
2. 主な機能
本プログラムは、段差検出の一連の処理を自動化し、結果を分かりやすく提示する以下の機能を提供する。
リアルタイム段差検出
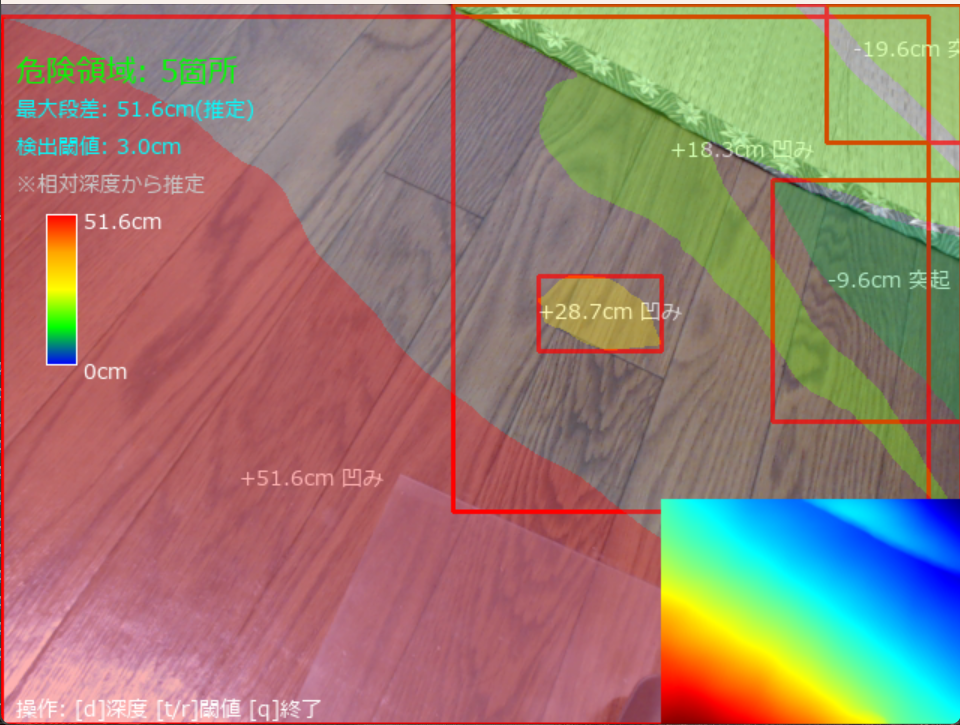
カメラ映像または動画ファイルを入力として、各フレームから段差を自動検出し、結果を画面に即座に表示する。処理は深度推定、床面推定、段差判定の順に実行され、検出された領域には赤い矩形が描画される。
段差高さの定量的推定
検出した各段差領域について、センチメートル単位での高さを推定する。推定値は床面からの距離の中央値に基づいており、さらに床面より上(突起)か下(凹み)かを判定して表示する。これにより、段差の危険度を数値的に評価できる。
段差の視覚的強調表示
段差の高さに応じて、青(低)から緑、黄、赤(高)へのグラデーションで色分け表示する。色の変化により、複数の段差が存在する場合でも、より注意が必要な箇所を直感的に識別できる。画面左側にはカラーバーが表示され、色と高さの対応関係を確認できる。
深度情報の可視化
dキーの操作により、通常のカメラ映像と深度マップのヒートマップ表示を切り替えられる。深度マップでは、近い物体は寒色系(青・緑)、遠い物体は暖色系(黄・赤)で表示される。この機能により、アルゴリズムが奥行きをどのように解釈しているかを確認でき、誤検出の原因分析に役立つ。
検出感度の調整機能
tキーとrキーにより、段差として判定する閾値を動的に変更できる。tキーで閾値を上げると大きな段差のみを検出し、rキーで下げると小さな凹凸も検出対象となる。環境や目的に応じて感度を調整することで、過検出や検出漏れを抑制できる。
処理履歴の記録
プログラム終了時に、処理したフレーム数、使用したハードウェア(CPU/GPU)、各フレームの検出結果をテキストファイル(result.txt)に自動保存する。この記録により、後から統計分析を行ったり、複数回の実行結果を比較したりできる。
3. 基本的な使い方
ステップ1: プログラムの起動と入力ソースの選択
プログラムを実行すると、コンソールに3つの選択肢が表示される。キーボードで数字を入力し、Enterキーを押して選択する。
- 0を選択: 保存済みの動画ファイルを使用する。選択後、ファイル選択ダイアログが表示されるので、対象となる動画ファイルを指定する。
- 1を選択: 接続されているウェブカメラからリアルタイムで映像を取得する。カメラが複数接続されている場合、通常は最初に認識されたカメラが使用される。
- 2を選択: プログラムに同梱されているサンプル動画を使用する。初めて実行する際の動作確認に適している。
ステップ2: 処理画面の表示と段差検出の開始
入力ソースの選択後、処理画面が表示され、段差検出が自動的に開始される。画面には入力映像が表示され、段差が検出されると該当領域が赤い矩形で囲まれる。矩形内には推定された高さ(cm単位)と、突起または凹みの種別が文字で表示される。
ステップ3: 画面表示情報の確認
画面左上には、現在の検出状況を示す情報が常時表示される。
- 危険領域の数: 現在のフレームで検出されている段差の総数
- 最大段差の高さ: 検出された段差のうち、最も高い(または深い)もののcm値
- 検出閾値: 段差と判定する高低差の基準値(cm単位)
画面左側には、段差の高さを色で表すカラーバーが表示され、青から赤への色の変化と高さの対応関係を示す。また、画面右下には深度マップのサムネイルが表示され、現在の深度推定結果を確認できる。
ステップ4: プログラムの終了と結果の保存
処理を終了する場合は、処理画面を選択した状態でキーボードのqキーを押す。プログラムは自動的に終了し、処理結果がresult.txtというテキストファイルに保存される。このファイルには、処理したフレーム数、使用したハードウェア、各フレームでの検出結果が記録される。
4. 便利な機能
深度マップ表示の切替(dキー)
通常のカメラ映像表示と、深度マップのヒートマップ表示を切り替える機能である。深度マップでは、カメラに近い位置が寒色系(青・緑)、遠い位置が暖色系(黄・赤)で表示される。この表示により、深度推定アルゴリズムが空間をどのように解釈しているかを視覚的に理解できる。特に、誤検出が発生した際に、その原因が深度推定の精度不足にあるのか、床面推定の問題なのかを切り分ける際に有用である。
検出閾値の調整(tキー・rキー)
段差として検出する高低差の基準値を、処理中にリアルタイムで変更できる機能である。tキーを押すと閾値が0.5cm刻みで増加し、より大きな段差のみが検出対象となる。これにより、床材の継ぎ目などの微細な凹凸を無視できる。逆に、rキーを押すと閾値が減少し、より小さな段差も検出されるようになる。環境や用途に応じて適切な閾値を設定することで、過検出と検出漏れのバランスを調整できる。現在の閾値は画面左上に常時表示される。
コンソール出力による詳細確認
処理画面とは別に、コンソールウィンドウには各フレームの処理結果がテキストで出力される。動画ファイルを処理する場合はフレーム番号、カメラを使用する場合はタイムスタンプとともに、検出された危険領域の数と最大段差の高さが表示される。この情報により、時系列での検出状況の変化を追跡できる。また、処理速度の目安としても利用できる。
処理結果の自動記録
プログラム終了時に生成されるresult.txtファイルには、セッション全体の処理情報が記録される。具体的には、総処理フレーム数、使用したハードウェア(CPUまたはGPU)の種類、そして各フレームにおける検出結果が含まれる。このファイルを保存しておくことで、後日の分析や、異なる設定での実行結果の比較ができる。複数回の実行結果を統計的に分析する際にも活用できる。
Python開発環境,ライブラリ類
ここでは、最低限の事前準備について説明する。機械学習や深層学習を行う場合は、NVIDIA CUDA、Visual Studio、Cursorなどを追加でインストールすると便利である。これらについては別ページ https://www.kkaneko.jp/cc/dev/aiassist.htmlで詳しく解説しているので、必要に応じて参照してください。
Python 3.12 のインストール
インストール済みの場合は実行不要。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要である。
REM Python をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements
REM Python のパス設定
set "PYTHON_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312"
set "PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312\Scripts"
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_PATH%" /M >nul
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" /M >nul【関連する外部ページ】
Python の公式ページ: https://www.python.org/
AI エディタ Windsurf のインストール
Pythonプログラムの編集・実行には、AI エディタの利用を推奨する。ここでは,Windsurfのインストールを説明する。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行して、Windsurfをシステム全体にインストールする。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
winget install --scope machine --id Codeium.Windsurf -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements【関連する外部ページ】
Windsurf の公式ページ: https://windsurf.com/
必要なライブラリをシステム領域にインストール
コマンドプロンプトを管理者として実行(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する
pip install -U torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126
pip install transformers opencv-python numpy pillow scipy scikit-learn opencv-contrib-python
床面段差検出プログラム
1. 概要
このプログラムは、単眼カメラの映像から床面の段差を自動検出する技術を実装したものである。人間の視覚が奥行きを認識するように、コンピュータビジョン技術を用いて2次元画像から3次元的な深度情報を推定し、床面における高低差を定量的に測定する。
処理は3つの段階で構成される。第1段階では、DPTモデルを用いて入力画像から深度マップを生成する。第2段階では、得られた深度情報を3次元点群に変換し、RANSAC平面推定により床面を数学的にモデル化する。第3段階では、推定した床面モデルからの距離を計算することで段差を検出し、その位置と高さを画面上に可視化する。
2. 主要技術
DPT (Dense Prediction Transformer)
Ranftl らが2021年に提案した深度推定モデルである[1]。深度推定とは、2次元画像の各ピクセルに対して、カメラからの距離(深度)を予測する技術である。従来、この課題には畳み込みニューラルネットワーク(CNN)が用いられてきたが、CNNは局所的な特徴抽出に優れる一方で、画像全体の大域的な文脈を捉えることに限界があった。
DPTは、自然言語処理で成功を収めたTransformerアーキテクチャを画像の密な予測タスクに適用することで、この問題を解決する。Transformerの自己注意機構により、画像内の離れた領域間の関係性を考慮しながら深度を推定できる。複数の大規模データセット(約140万枚の画像)で事前学習されており、単一のRGB画像から相対的な深度マップを生成する。ここで「相対的」とは、絶対的な距離ではなく、画像内での相対的な遠近関係を表すことを意味する。
RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus)
Fischler と Bolles が1981年に開発したロバストなモデル推定アルゴリズムである[2]。実世界のデータには、測定誤差(ノイズ)だけでなく、モデルに全く適合しない外れ値(アウトライア)が含まれることが多い。例えば、床面の点群データには、床上に置かれた物体や壁面からの点が混入する。従来の最小二乗法などの手法は、これらの外れ値の影響を大きく受け、不正確な結果を生じる。
RANSACは、ランダムサンプリングと多数決の原理を組み合わせることで、この問題に対処する。具体的には、データからランダムに最小限の点をサンプリングし、それらからモデル(本プログラムでは平面)を仮定する。次に、このモデルに適合する点(インライア)の数を数える。この過程を繰り返し、最も多くのインライアを持つモデルを最良の推定結果として採用する。本プログラムでは、深度マップから生成した3次元点群に対してRANSACを適用し、床面を表す平面方程式のパラメータを推定する。
3. 技術的特徴
- 相対深度からの距離推定
DPTが出力する深度は相対値であり、そのままでは実世界の距離(センチメートル単位)を表さない。本プログラムでは、単眼カメラの制約を考慮し、逆深度の概念を利用する。逆深度は、カメラから物体までの距離の逆数であり、遠方ほど値が小さくなる性質を持つ。この逆深度分布の中央値を参照距離(本実装では150cm)に対応付けることで、相対深度を推定距離に変換する。絶対的な精度には限界があるが、段差の有無と相対的な高さの判定には十分である。
- 連結成分を考慮したRANSAC平面推定
標準的なRANSACは、インライア数のみを評価基準とする。しかし、床面は空間的に連続した領域であるべきという幾何学的制約がある。本実装では、scikit-learnのRANSACRegressorによる平面推定に加えて、インライアを画像座標上に投影し、連結成分解析を適用する。最大の連結成分の面積をスコアとすることで、空間的に分散した外れ値ではなく、連続した床面領域を優先的に選択する。
- 時間的平滑化による安定化
動画の各フレームを独立に処理すると、推定される床面の向きが微妙に変動し、検出結果が不安定になる問題がある。本プログラムでは、連続フレーム間で床面法線ベクトルに指数平滑化(重み0.8)を適用する。さらに、初期フレームで法線の向きをカメラの光軸方向に固定し、以降のフレームでは前フレームとの内積が負にならないよう符号を制御する。これにより、床面の向きが突然反転する現象を防ぎ、安定した段差検出を実現する。
- 適応的閾値処理
段差として検出すべき高低差の閾値は、環境や用途によって異なる。本プログラムでは、初期値として5cm相当の閾値を設定しつつ、ユーザーがキー操作によりリアルタイムで調整できる機能を提供する。これにより、小さな凹凸を無視して大きな段差のみを検出する、あるいは逆に微細な高低差まで検出するといった、状況に応じた調整が可能である。
- 多段階フィルタリング
深度推定の結果には、センサノイズや推定誤差が含まれる。これらをそのまま使用すると、誤検出が増加する。本プログラムでは、深度マップに対して複数のフィルタを段階的に適用する。メディアンフィルタでノイズを除去し、バイラテラルフィルタでエッジを保存しながら平滑化する。さらに、検出後の段差領域に対して形態学的処理(オープニング・クロージング)を適用し、孤立した小領域を除去する。
4. 実装の特色
本プログラムは、研究段階の技術を実用的なアプリケーションとして実装することを目的としており、以下の特色を持つ。
入力に関しては、動画ファイル、ウェブカメラ、サンプル動画の3つのソースから選択できる。これにより、事前に撮影した動画の解析だけでなく、リアルタイムでの段差検出も行える。
出力に関しては、検出した段差領域ごとに高さを推定し、その値を画面上に表示する。高さの推定には、その領域内の点群から床面までの距離の中央値を用いる。さらに、床面より上か下かを判定し、「突起」または「凹み」として区別する。視覚的な理解を助けるため、段差の高さに応じて青(低い)から赤(高い)へのグラデーションで色分け表示する。
ユーザーインターフェースでは、通常のカメラ映像と深度マップのヒートマップを切り替え表示できる機能を提供する。深度マップ表示により、検出アルゴリズムがどのように奥行きを認識しているかを視覚的に確認できる。
処理の効率化に関しては、利用可能なハードウェアに応じてGPUまたはCPUを自動選択する。GPU使用時には自動混合精度(AMP)を適用し、計算速度と精度のバランスを取る。処理結果は終了時にテキストファイルへ自動保存され、後からの検証や統計分析に利用できる。
5. 参考文献
[1] Ranftl, R., Bochkovskiy, A., & Koltun, V. (2021). Vision Transformers for Dense Prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 12179-12188). https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13413
[2] Fischler, M. A., & Bolles, R. C. (1981). Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Communications of the ACM, 24(6), 381-395. https://doi.org/10.1145/358669.358692
ソースコード
# プログラム名: 床面段差検出プログラム - DPT深度推定による危険箇所可視化
# 特徴技術名: DPT (Dense Prediction Transformer) + CC-RANSAC
# 出典: Ranftl, R., et al. (2021). Vision Transformers for Dense Prediction. ICCV 2021.
# 特徴機能: Vision Transformerベースアーキテクチャによる相対深度推定 + 連結成分考慮のRANSAC平面検出
# 学習済みモデル: DPT-Large、相対深度推定が可能なTransformerベースモデル、URL: https://huggingface.co/Intel/dpt-large
# 方式設計:
# - 関連利用技術: OpenCV (動画処理), NumPy (数値計算), Transformers (モデル読み込み), Tkinter (GUI), scikit-learn (RANSAC)
# - 入力と出力: 入力: 動画(ユーザは「0:動画ファイル,1:カメラ,2:サンプル動画」のメニューで選択)、出力: 処理結果が画像化されOpenCV画面でリアルタイム表示
# - 処理手順: RGB画像入力→DPTによる相対深度推定→3D点群生成→CC-RANSAC平面推定→適応的閾値による段差検出→危険領域の可視化
# - 前処理、後処理: 前処理: DPTImageProcessorによる自動前処理、後処理: エッジ保存フィルタ、適応的深度正規化
# - 追加処理: 深度ヒストグラムベースの動的閾値設定、連結成分を考慮したRANSAC、ロバストな時間的平滑化、段差高さ推定
# 前準備:
# - pip install -U torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126
# - pip install transformers opencv-python numpy pillow scipy scikit-learn opencv-contrib-python huggingface_hub timm safetensors
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
from scipy.ndimage import median_filter
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
from transformers import DPTImageProcessor, DPTForDepthEstimation
from sklearn.linear_model import RANSACRegressor, LinearRegression
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
import time
import urllib.request
from datetime import datetime
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 調整可能な設定値
DISTANCE_THRESHOLD = 0.05 # 平面からの距離閾値(正規化単位、後でcm換算)←幾何誤差吸収のため初期値を約5cm相当に
DANGER_AREA_SIZE = 500 # 危険領域とみなす最小面積(px)
RANSAC_ITERATIONS = 100 # RANSAC反復回数
TEMPORAL_SMOOTHING = 0.8 # 法線・dの時間的平滑化の重み
# フィルタリング設定
BILATERAL_D = 5
BILATERAL_SIGMA_COLOR = 50
BILATERAL_SIGMA_SPACE = 50
MEDIAN_KERNEL_SIZE = 3
# カメラパラメータ(推定値)
CAMERA_FOV_HORIZONTAL = 60.0 # 水平視野角(度)
TYPICAL_FLOOR_HEIGHT = 150.0 # 参照距離(cm)
# フラグ
SHOW_DEPTH_MAP = False
# 乱数シード
RANDOM_SEED = 42
np.random.seed(RANDOM_SEED)
# GPU/CPU自動選択
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(f'デバイス: {str(device)}')
# GPU使用時の最適化
if device.type == 'cuda':
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
# AMP前提: モデル重みはfloat32のまま、計算はAMPで半精度化
torch_dtype = torch.float32
# DPTモデル読み込み(snapshot_downloadで取得したローカルスナップショットを使用、safetensorsを強制)
print('深度推定モデルを読み込み中...')
local_dir = snapshot_download(
"Intel/dpt-large",
allow_patterns=["*.json", "*.safetensors"] # safetensorsと設定のみ取得
)
processor = DPTImageProcessor.from_pretrained(local_dir)
model = DPTForDepthEstimation.from_pretrained(local_dir, use_safetensors=True).to(device)
model.eval()
print('モデルの読み込みが完了しました')
print('')
# プログラムの概要表示
print('=== 床面段差検出プログラム(段差高さ推定機能付き) ===')
print('DPTによる相対深度推定とRANSACを使用して床面の段差や危険箇所を検出します')
print('')
print('【重要な注意事項】')
print(' - DPTモデルは相対深度(relative depth)を出力します')
print(' - 表示される段差の高さ(cm)は推定値です')
print(' - 単眼カメラのため絶対的な距離は不明で、相対的な深度差から推定しています')
print('')
print('【その他の注意事項】')
print(' - 初回実行時はモデルのダウンロードに時間がかかります')
print(' - GPUを使用する場合はCUDA対応環境が必要です')
print('')
# 結果記録用
frame_count = 0
results_log = []
prev_plane_params = None
distance_threshold_current = DISTANCE_THRESHOLD
# 日本語表示用フォント設定
FONT_PATH = 'C:/Windows/Fonts/meiryo.ttc'
FONT_SIZE = 20
try:
font = ImageFont.truetype(FONT_PATH, FONT_SIZE)
font_small = ImageFont.truetype(FONT_PATH, 14)
except:
font = None
font_small = None
print('日本語フォントの読み込みに失敗しました。英語表示になります。')
def get_gradient_color(value, min_val, max_val):
"""
値を0-1に正規化して、青→緑→黄→赤のグラデーションカラー(BGR)を返す
"""
if max_val - min_val < 1e-6:
return (0, 255, 0)
normalized = (value - min_val) / (max_val - min_val)
normalized = np.clip(normalized, 0, 1)
if normalized < 0.25:
ratio = normalized * 4
b = int(255 * (1 - ratio))
g = int(255 * ratio)
r = 0
elif normalized < 0.5:
ratio = (normalized - 0.25) * 4
b = 0
g = 255
r = int(255 * ratio)
elif normalized < 0.75:
ratio = (normalized - 0.5) * 4
b = 0
g = int(255 * (1 - ratio * 0.35))
r = 255
else:
ratio = (normalized - 0.75) * 4
b = 0
g = int(165 * (1 - ratio))
r = 255
return (b, g, r)
def compute_3d_points(depth_map_cm, image_width, image_height, fov_horizontal=60.0):
"""
深度マップ(cm)から3D点群(cm)を生成する
"""
focal_length_px = image_width / (2 * np.tan(np.radians(fov_horizontal / 2)))
cx = image_width / 2
cy = image_height / 2
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(image_width), np.arange(image_height))
z = depth_map_cm
x = (xx - cx) * z / focal_length_px
y = (yy - cy) * z / focal_length_px
points_3d = np.stack([x, y, z], axis=-1)
return points_3d
def simple_plane_ransac_metric(points_3d, max_iterations=100, threshold_cm=2.0):
"""
3点サンプリングによるRANSAC平面推定(単位: cm)
戻り値: (normal(正規化), d), inlier_indices(flatインデックス)
"""
points_flat = points_3d.reshape(-1, 3)
valid_mask = ~np.isnan(points_flat).any(axis=1) & (points_flat[:, 2] > 0)
valid_points = points_flat[valid_mask]
if len(valid_points) < 100:
return None, []
best_inliers = []
best_plane = None
for _ in range(max_iterations):
sample_idx = np.random.choice(len(valid_points), 3, replace=False)
p1, p2, p3 = valid_points[sample_idx]
v1 = p2 - p1
v2 = p3 - p1
normal = np.cross(v1, v2)
n_norm = np.linalg.norm(normal)
if n_norm < 1e-6:
continue
normal = normal / n_norm
d = -np.dot(normal, p1)
distances = np.abs(np.dot(valid_points, normal) + d)
inliers = np.where(distances < threshold_cm)[0]
if len(inliers) > len(best_inliers):
best_inliers = inliers
best_plane = (normal, d)
if best_plane is None:
return None, []
original_indices = np.where(valid_mask)[0][best_inliers]
return best_plane, original_indices
def detect_floor_plane_metric(points_3d, image_height, image_width):
"""
最大インライア平面を床面候補として返す
"""
best_plane = None
best_inliers = []
for _ in range(3):
plane_params, inlier_indices = simple_plane_ransac_metric(
points_3d,
max_iterations=RANSAC_ITERATIONS,
threshold_cm=2.0
)
if plane_params is not None and len(inlier_indices) > len(best_inliers):
best_plane = plane_params
best_inliers = inlier_indices
return best_plane, best_inliers
def detect_floor_plane_metric_sklearn_cc(points_3d, image_height, image_width,
residual_threshold_cm=2.0, max_trials=RANSAC_ITERATIONS, attempts=5):
"""
scikit-learn の RANSACRegressor による平面推定(z = a x + b y + c)を行い、
画像座標上でインライアの最大連結成分(CC)の面積をスコアとして評価する。
戻り値: (plane_params=(normal(正規化), d), inlier_indices(flatインデックス))
"""
points_flat = points_3d.reshape(-1, 3)
valid_mask = ~np.isnan(points_flat).any(axis=1) & (points_flat[:, 2] > 0)
if valid_mask.sum() < 100:
return None, []
X = points_flat[valid_mask][:, :2] # (x, y)
y = points_flat[valid_mask][:, 2] # z
valid_indices = np.where(valid_mask)[0]
best_score = -1.0
best_plane = None
best_inliers_flat = []
for i in range(attempts):
try:
ransac = RANSACRegressor(
estimator=LinearRegression(),
residual_threshold=residual_threshold_cm,
max_trials=max_trials,
random_state=RANDOM_SEED + i
)
ransac.fit(X, y)
except Exception:
continue
inlier_mask = ransac.inlier_mask_.astype(bool) if hasattr(ransac, "inlier_mask_") else None
if inlier_mask is None or inlier_mask.sum() < 50:
continue
# 平面係数 z = a x + b y + c
a, b = float(ransac.estimator_.coef_[0]), float(ransac.estimator_.coef_[1])
c = float(ransac.estimator_.intercept_)
n = np.array([a, b, -1.0], dtype=np.float32)
n_norm = np.linalg.norm(n)
if n_norm < 1e-6:
continue
normal = n / n_norm
d = c / n_norm # n·p + d = 0 における d
# インライアの2D連結成分スコア
inlier_flat_idx = valid_indices[inlier_mask]
mask2d = np.zeros((image_height, image_width), dtype=np.uint8)
ys, xs = np.unravel_index(inlier_flat_idx, (image_height, image_width))
mask2d[ys, xs] = 255
num_labels, labels, stats, centroids = cv2.connectedComponentsWithStats(mask2d, connectivity=8)
if num_labels <= 1:
score = 0.0
else:
# 背景(0)以外の最大成分面積
score = float(stats[1:, cv2.CC_STAT_AREA].max())
if score > best_score:
best_score = score
best_plane = (normal, d)
best_inliers_flat = inlier_flat_idx
if best_plane is None:
return None, []
return best_plane, best_inliers_flat
def calculate_step_heights(points_3d, plane_params, danger_mask):
"""
危険領域ごとに段差高さを計算する。
代表値は |距離| の中央値(cm)。符号は median(n·p + d) の符号で与える。
戻り値: { region_id: {'center':(cx,cy), 'median_abs_height_cm':..., 'signed_median_cm':..., 'area':..., 'contour':...} }
"""
if plane_params is None:
return {}
normal, d = plane_params
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(
danger_mask.astype(np.uint8),
cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE
)
step_heights = {}
for i, contour in enumerate(contours):
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
if area > DANGER_AREA_SIZE:
mask = np.zeros(danger_mask.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.drawContours(mask, [contour], -1, 255, -1)
masked_points = points_3d[mask > 0]
valid_points = masked_points[~np.isnan(masked_points).any(axis=1)]
if len(valid_points) > 0:
distances = np.dot(valid_points, normal) + d # 符号付き距離(cm)
abs_median = float(np.median(np.abs(distances)))
signed_median = float(np.median(distances))
M = cv2.moments(contour)
if M["m00"] != 0:
cx = int(M["m10"] / M["m00"])
cy = int(M["m01"] / M["m00"])
step_heights[i] = {
'center': (cx, cy),
'median_abs_height_cm': abs_median,
'signed_median_cm': signed_median,
'area': area,
'contour': contour
}
return step_heights
def add_text_to_frame(frame, text, position, font_obj, font_size=20, color=(0, 255, 0)):
"""
OpenCV画像に日本語テキストを追加する。
colorはBGR指定。Pillow描画時にRGBへ変換して用いる。
"""
if font_obj is None:
cv2.putText(frame, text, position, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
font_size/30, color, max(1, font_size//15))
return frame
img_pil = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img_pil)
draw.text(position, text, font=font_obj, fill=color[::-1]) # BGR→RGB
frame = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(img_pil), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
return frame
def format_step_label(signed_median_cm, median_abs_height_cm):
"""
段差ラベル文字列を生成する(符号と「突起/凹み」を含む)
"""
sign = '-' if signed_median_cm < 0 else '+'
label = '突起' if signed_median_cm < 0 else '凹み'
return f"{sign}{median_abs_height_cm:.1f}cm {label}"
def make_depth_colormap(depth_map_normalized, thumbnail_size=(200, 150)):
"""
深度の擬似カラー画像とサムネイルを生成する
"""
depth_vis = (depth_map_normalized * 255).astype(np.uint8)
depth_vis_color = cv2.applyColorMap(depth_vis, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
small_depth = cv2.resize(depth_vis_color, thumbnail_size)
return depth_vis_color, small_depth
def annotate_step_region(base_frame, overlay_frame, step_info, color, font_small, depth_mode=False):
"""
ステップ領域の矩形・塗りつぶし・ラベル描画を行う
"""
contour = step_info['contour']
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour)
# 深度マップ表示でない場合は領域塗りつぶし(重ね合わせ用)
if not depth_mode and overlay_frame is not None:
cv2.drawContours(overlay_frame, [contour], -1, color, -1)
# 矩形枠
cv2.rectangle(base_frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# ラベル描画
cx, cy = step_info['center']
height_text = format_step_label(step_info['signed_median_cm'], step_info['median_abs_height_cm'])
add_text_to_frame(base_frame, height_text, (cx - 40, cy - 10), font_small, color=(255, 255, 255))
return base_frame
def draw_hud(frame, danger_count, current_max_height, distance_threshold_current, font, font_small, original_height):
"""
画面左上のHUD(危険領域数、最大段差、検出閾値、注意書き、操作ヘルプ)とカラーバーを描画する
"""
frame = add_text_to_frame(frame, f'危険領域: {danger_count}箇所', (10, 30), font, color=(0, 255, 0))
if danger_count > 0:
frame = add_text_to_frame(frame, f'最大段差: {current_max_height:.1f}cm(推定)', (10, 60), font_small, color=(255, 255, 0))
frame = add_text_to_frame(frame, f'検出閾値: {distance_threshold_current * 100:.1f}cm', (10, 85), font_small, color=(255, 255, 0))
frame = add_text_to_frame(frame, "※相対深度から推定", (10, 110), font_small, color=(200, 200, 200))
frame = add_text_to_frame(frame, "操作: [d]深度 [t/r]閾値 [q]終了", (10, original_height - 20), font_small, color=(255, 255, 255))
# カラーバー
if current_max_height > 0:
bar_x, bar_y, bar_width, bar_height = 30, 140, 20, 100
# グラデーションカラーバーを描画する(BGR)
for i in range(bar_height):
value = current_max_height * (1 - i / bar_height)
color = get_gradient_color(value, 0, current_max_height)
cv2.line(frame, (bar_x, bar_y + i), (bar_x + bar_width, bar_y + i), color, 1)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (bar_x, bar_y), (bar_x + bar_width, bar_y + bar_height), (255, 255, 255), 1)
frame = add_text_to_frame(frame, f"{current_max_height:.1f}cm",
(bar_x + bar_width + 5, bar_y - 5), font_small, color=(255, 255, 255))
frame = add_text_to_frame(frame, "0cm",
(bar_x + bar_width + 5, bar_y + bar_height - 5), font_small, color=(255, 255, 255))
return frame
def video_frame_processing(frame):
"""
1フレームを処理して結果フレームを返す。
・初期フレームで床法線の向きをカメラ方向([0,0,1])にそろえる。
・以降は符号反転を防ぎ、時間平滑化を適用する。
・危険領域の代表高さは |距離| の中央値(cm)を用いる。
"""
global frame_count, prev_plane_params, SHOW_DEPTH_MAP, distance_threshold_current
current_time = time.time()
frame_count += 1
original_height, original_width = frame.shape[:2]
# DPT推論
rgb_frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
pil_image = Image.fromarray(rgb_frame)
inputs = processor(images=pil_image, return_tensors='pt')
inputs = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
use_amp = (device.type == 'cuda')
with torch.no_grad():
if use_amp:
# CUDA環境では自動混合精度により半精度で計算する
with torch.autocast(device_type='cuda', dtype=torch.float16):
outputs = model(**inputs)
else:
outputs = model(**inputs)
depth = outputs.predicted_depth
# 出力をfloat32へ明示し、OpenCV互換のndarrayへ
depth_map_raw = depth.squeeze().detach().float().cpu().numpy()
# 幾何用は正規化を使わず、rawのまま平滑化してからZを作る(平面を曲面化しないため)
depth_map_denoised = median_filter(depth_map_raw, size=MEDIAN_KERNEL_SIZE)
depth_map_denoised = cv2.bilateralFilter(
depth_map_denoised.astype(np.float32),
BILATERAL_D, BILATERAL_SIGMA_COLOR, BILATERAL_SIGMA_SPACE
)
# 幾何用のサイズを入力フレームに合わせる
depth_map_denoised = cv2.resize(depth_map_denoised, (original_width, original_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# 可視化用はmin-max正規化を使う(幾何には用いない)
dmin, dmax = float(np.min(depth_map_denoised)), float(np.max(depth_map_denoised))
if dmax - dmin > 1e-6:
depth_vis_norm = (depth_map_denoised - dmin) / (dmax - dmin)
else:
depth_vis_norm = np.ones_like(depth_map_denoised, dtype=np.float32) * 0.5
# 相対→推定cm(逆深度仮定: Z ≈ 1/(ε+relative_depth_raw))
eps = 1e-6
inv_z = 1.0 / (depth_map_denoised + eps)
valid = np.isfinite(inv_z) & (inv_z > 0)
median_z = np.median(inv_z[valid]) if np.any(valid) else 0.0
if median_z > 0:
scale = TYPICAL_FLOOR_HEIGHT / median_z
depth_map_cm = inv_z * scale
else:
depth_map_cm = inv_z * TYPICAL_FLOOR_HEIGHT
# 3D点群
points_3d = compute_3d_points(
depth_map_cm, original_width, original_height, CAMERA_FOV_HORIZONTAL
)
# 平面推定(scikit-learn RANSAC + 連結成分スコア)閾値を緩めに(5cm)
plane_params, floor_inlier_indices = detect_floor_plane_metric_sklearn_cc(
points_3d, original_height, original_width,
residual_threshold_cm=5.0, max_trials=RANSAC_ITERATIONS, attempts=5
)
danger_mask = np.zeros((original_height, original_width), dtype=bool)
points_flat = points_3d.reshape(-1, 3)
if plane_params is not None and len(floor_inlier_indices) > 0:
normal, d = plane_params
inlier_points = points_flat[floor_inlier_indices]
# 初期フレームで法線の向きをカメラ方向に固定(view_dir=[0,0,1])
if prev_plane_params is None:
view_dir = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 1.0], dtype=np.float32)
if np.dot(normal, view_dir) < 0:
normal = -normal
d = -d
# 平面式の整合を保つため、dはインライアから再計算
d = -np.median(np.dot(inlier_points, normal))
plane_params = (normal, d)
prev_plane_params = plane_params
else:
prev_normal, prev_d = prev_plane_params
# 符号反転防止
if np.dot(normal, prev_normal) < 0:
normal = -normal
d = -d
# 法線のみ時間平滑化し正規化
smoothed_normal = TEMPORAL_SMOOTHING * prev_normal + (1 - TEMPORAL_SMOOTHING) * normal
smoothed_normal = smoothed_normal / np.linalg.norm(smoothed_normal)
# dはインライア集合に対する median(n·p) から再算出(整合性維持)
smoothed_d = -np.median(np.dot(inlier_points, smoothed_normal))
plane_params = (smoothed_normal, smoothed_d)
normal, d = plane_params
prev_plane_params = plane_params
# 距離(cm、符号なしは閾値用)
distances = np.abs(np.dot(points_flat, normal) + d).reshape(original_height, original_width)
# 危険領域マスク(閾値はcm換算)
threshold_cm = distance_threshold_current * 100.0
danger_mask = (distances > threshold_cm) & (depth_map_cm > 0) & ~np.isnan(distances)
# 床面インライアを除外
floor_mask = np.zeros((original_height, original_width), dtype=bool)
floor_pixels = np.unravel_index(floor_inlier_indices, (original_height, original_width))
floor_mask[floor_pixels] = True
danger_mask = danger_mask & ~floor_mask
# 形態学的処理
danger_mask_uint8 = danger_mask.astype(np.uint8) * 255
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (5, 5))
danger_mask_uint8 = cv2.morphologyEx(danger_mask_uint8, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
danger_mask_uint8 = cv2.morphologyEx(danger_mask_uint8, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
# 段差高さ算出(中央値)
step_heights = calculate_step_heights(points_3d, plane_params, danger_mask_uint8)
# 可視化準備
current_max_height = 0.0
if step_heights:
current_max_height = max(s['median_abs_height_cm'] for s in step_heights.values())
# 深度ヒートマップを一度だけ生成(可視化用の正規化を使用)
depth_vis_color, small_depth = make_depth_colormap(depth_vis_norm, thumbnail_size=(200, 150))
if SHOW_DEPTH_MAP:
# 深度マップのヒートマップ
result_frame = depth_vis_color.copy()
for step_id, step_info in step_heights.items():
# 深度マップ表示モードでは塗りつぶしなし、矩形とラベルのみ
annotate_step_region(result_frame, None, step_info, (0, 0, 0), font_small, depth_mode=True)
else:
result_frame = frame.copy()
overlay = frame.copy()
for step_id, step_info in step_heights.items():
mag_cm = step_info['median_abs_height_cm']
color = get_gradient_color(mag_cm, 0, current_max_height if current_max_height > 0 else 1.0)
annotate_step_region(result_frame, overlay, step_info, color, font_small, depth_mode=False)
cv2.addWeighted(overlay, 0.3, result_frame, 0.7, 0, result_frame)
# 深度マップのサムネイルを右下に表示(フレームサイズに応じて安全に貼り付け)
sh, sw = small_depth.shape[:2]
sh_clip = min(sh, original_height)
sw_clip = min(sw, original_width)
y1_dst = original_height - sh_clip
x1_dst = original_width - sw_clip
y1_src = sh - sh_clip
x1_src = sw - sw_clip
result_frame[y1_dst:original_height, x1_dst:original_width] = small_depth[y1_src:sh, x1_src:sw]
danger_count = len(step_heights)
# HUD描画を一箇所に集約
result_frame = draw_hud(result_frame, danger_count, current_max_height, distance_threshold_current, font, font_small, original_height)
# 結果テキスト
if danger_count > 0:
result = f'危険領域: {danger_count}箇所, 最大段差: {current_max_height:.1f}cm(推定)'
else:
result = f'危険領域: 0箇所'
return result_frame, result, current_time
# メニュー表示
print('0: 動画ファイル')
print('1: カメラ')
print('2: サンプル動画')
choice = input("選択: ")
if choice == '0':
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
path = filedialog.askopenfilename()
if not path:
exit()
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(path)
elif choice == '1':
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0, cv2.CAP_DSHOW)
if not cap.isOpened():
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_BUFFERSIZE, 1)
else:
# サンプル動画ダウンロード・処理
SAMPLE_URL = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/opencv/opencv/master/samples/data/vtest.avi'
SAMPLE_FILE = 'vtest.avi'
urllib.request.urlretrieve(SAMPLE_URL, SAMPLE_FILE)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(SAMPLE_FILE)
if not cap.isOpened():
print('動画ファイル・カメラを開けませんでした')
exit()
# メイン処理
print('\n=== 動画処理開始 ===')
print('操作方法:')
print(' q キー: プログラム終了')
print(' d キー: 深度マップ表示切替')
print(' t キー: 閾値を増加(段差検出を厳しく)')
print(' r キー: 閾値を減少(段差検出を緩く)')
try:
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
MAIN_FUNC_DESC = "床面段差検出"
processed_frame, result, current_time = video_frame_processing(frame)
cv2.imshow(MAIN_FUNC_DESC, processed_frame)
if choice == '1': # カメラの場合
print(datetime.fromtimestamp(current_time).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f")[:-3], result)
else: # 動画ファイルの場合
print(frame_count, result)
results_log.append(result)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if key == ord('q'):
break
elif key == ord('d'):
SHOW_DEPTH_MAP = not SHOW_DEPTH_MAP
mode = "深度マップ" if SHOW_DEPTH_MAP else "通常"
print(f"表示モード切替: {mode}")
elif key == ord('t'):
distance_threshold_current = min(distance_threshold_current + 0.005, 0.1)
print(f"検出閾値を増加: {distance_threshold_current * 100:.1f}cm(推定)")
elif key == ord('r'):
distance_threshold_current = max(distance_threshold_current - 0.005, 0.01)
print(f"検出閾値を減少: {distance_threshold_current * 100:.1f}cm(推定)")
finally:
print('\n=== プログラム終了 ===')
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if results_log:
with open('result.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write('=== 結果 ===\n')
f.write(f'処理フレーム数: {frame_count}\n')
f.write(f'使用デバイス: {str(device).upper()}\n')
if device.type == 'cuda':
f.write(f'GPU: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)}\n')
f.write('\n')
f.write('\n'.join(results_log))
print(f'\n処理結果をresult.txtに保存しました')
実験・研究スキルの基礎:Windows で学ぶ床面段差検出実験
1. 実験・研究のスキル構成要素
実験や研究を行うには、以下の5つの構成要素を理解する必要がある。
1.1 実験用データ
このプログラムでは動画ファイルまたはカメラ映像が実験用データである。
1.2 実験計画
何を明らかにするために実験を行うのかを定める。
計画例:
- 距離閾値が段差検出数に与える影響を確認する
- 深度推定の精度が環境条件によってどう変化するかを観察する
- 床面推定の安定性を評価する
- 誤検出を最小化するための閾値設定を見つける
- 特定の段差(突起、凹み)を確実に検出する条件を探る
1.3 プログラム
実験を実施するためのツールである。このプログラムはDPT深度推定モデルとRANSAC平面推定を使用している。
- プログラムの機能を理解して活用することが基本である
- 基本となるプログラムを出発点として、将来、様々な機能を自分で追加することができる
1.4 プログラムの機能
このプログラムは閾値操作で段差検出を制御する。
入力ソース:
- 動画ファイル、カメラ、サンプル動画から選択
調整可能なパラメータ:
- 検出閾値:床面からの距離の閾値
出力情報:
- 入力映像と検出結果の統合表示
- 検出された段差の数と最大段差の高さ
- 段差領域ごとの推定高さと種別(突起または凹み)
- 深度マップのサムネイル表示
キー操作:
- tキー:閾値を増加
- rキー:閾値を減少
- dキー:通常表示と深度マップ表示の切替
- qキー:プログラム終了
1.5 検証(結果の確認と考察)
プログラムの実行結果を観察し、パラメータの影響を考察する。
基本認識:
- 閾値を変えると結果が変わる。その変化を観察することが実験である
- 表示される段差の高さは、相対深度を距離に変換した推定値である
- 検出精度は照明条件や床面の材質によって変化する
観察のポイント:
- 検出される段差の数はどう変化するか
- 誤検出(段差でない箇所の検出)は発生しているか
- 見逃し(実際の段差の未検出)は発生しているか
- 推定される段差の高さは実測値と比較して妥当か
- 床面推定は安定しているか
- 照明条件や撮影角度は結果に影響するか
2. 間違いの原因と対処方法
2.1 プログラムのミス(人為的エラー)
プログラムがエラーで停止する
- 原因:必要なライブラリがインストールされていない、モデルのダウンロードに失敗している
- 対処方法:エラーメッセージを確認し、pipコマンドで必要なライブラリを再インストールする
カメラが開けない
- 原因:カメラが他のアプリケーションで使用されている、またはカメラが接続されていない
- 対処方法:他のカメラアプリを終了するか、動画ファイルモードで実行する
処理が極端に遅い
- 原因:GPUが利用できていない、高解像度の動画を処理している
- 対処方法:CUDA対応環境を確認する。低解像度の動画ファイルを使用するか、低解像度のカメラに変更する
2.2 期待される結果が得られない場合
閾値を変えても検出数が変化しない
- 原因:映像内に明確な段差が存在しない、または閾値の変化幅が小さすぎる
- 対処方法:tキーとrキーを用いて閾値を大きく変化させる。変化がない場合は段差を含む別の映像で実験する
明らかに存在する段差が検出されない
- 原因:閾値が高すぎる、深度推定の精度が不十分、照明条件が悪い
- 対処方法:rキーで閾値を下げる。照明を改善する。カメラの角度を調整する
床面でない箇所(壁や物体)が段差として検出される
- 原因:床面推定が不安定、閾値が低すぎる
- 対処方法:tキーで閾値を上げる。カメラを床面が広く映る位置に調整する
推定高さが実測値と大きく異なる
- 原因:相対深度からの変換における仮定(参照距離150cm)が実環境と合っていない
- 対処方法:推定値は参考値として扱う。正確な測定には計測器具を使用する。相対的な高低差の比較には利用できる
3. 実験レポートのサンプル
検出閾値の最適化
実験目的:
テスト環境において段差を確実に検出しながら、誤検出を最小化するための閾値を見つける。
実験計画:
段差を含む動画を用い、閾値を変化させて検出性能を評価する。
実験方法:
プログラムを実行し、tキーとrキーで閾値を調整しながら以下の基準で評価する:
- 正検出数:正しく検出された段差の数
- 誤検出数:誤って検出された数
- 見逃し数:検出されなかった段差の数
- 推定精度:推定高さと実測値の差
実験結果:
| 閾値(cm) | 検出総数 | 正検出数 | 誤検出数 | 見逃し数 | 総合評価 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xxxx | x | x | x | x | x |
| xxxx | x | x | x | x | x |
| xxxx | x | x | x | x | x |
| xxxx | x | x | x | x | x |
考察:
- (例文)閾値xxxxでは検出感度が高く、床材の継ぎ目なども段差として検出され誤検出が多かった
- (例文)閾値xxxxでは段差を安定して検出でき、誤検出も少なかった
- (例文)閾値xxxx以上では大きな段差のみが検出され、小さな段差は見逃しが発生した
- (例文)閾値を上げるほど誤検出は減るが、見逃しも増えるというトレードオフの関係が確認できた
- (例文)推定高さは実測値に対してxxxxの誤差があり、絶対値としての精度には限界があることが分かった
結論:
(例文)本実験環境においては、閾値xxxxが最もバランスの取れた設定であった。(例文)小さな段差も検出したい場合はxxxx、大きな段差のみに注目する場合はxxxxが適切である。(例文)また、推定高さは参考値として扱い、正確な測定が必要な場合は別途計測器具を使用すべきである。(例文)単眼カメラによる深度推定には限界があるが、段差の存在と位置の迅速な把握には有効であることが確認できた。
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)